在 ASP.NET Core 或 ASP.NET 5 中部署百度编辑器请跳转此文。
本文记录百度编辑器 ASP.NET 版的部署过程,对其它语言版本也有一定的参考价值。
【2020.02.21 重新整理】
下载
从 GitHub 下载最新发布版本:https://github.com/fex-team/ueditor/releases
按编码分有 gbk 和 utf8 两种版本,按服务端编程语言分有 asp、jsp、net、php 四种版本,按需下载。
目录介绍
以 v1.4.3.3 utf8-net 为例,

客户端部署
本例将上述所有目录和文件拷贝到网站目录 /libs/ueditor/ 下。
当然也可以引用 CDN 静态资源,但会遇到诸多跨域问题,不建议。
在内容编辑页面引入:
<script src="/libs/ueditor/ueditor.config.js"></script>
<script src="/libs/ueditor/ueditor.all.min.js"></script>在内容显示页面引入:
<script src="/libs/ueditor/ueditor.parse.min.js"></script>如需修改编辑器资源文件根路径,参 ueditor.config.js 文件内顶部文件。(一般不需要单独设置)
如果使用 CDN,那么在初始化 UE 实例的时候应配置 serverUrl 值(即 controller.ashx 所在路径)。
客户端配置
初始化 UE 实例:
var ue = UE.getEditor('tb_content', {
// serverUrl: '/libs/ueditor/net/controller.ashx', // 指定服务端接收文件路径
initialFrameWidth: '100%'
});其它参数见官方文档,或 ueditor.config.js 文件。
服务端部署
net 目录是 ASP.NET 版的服务端程序,用来实现接收上传的文件等功能。
本例中在网站中的位置是 /libs/ueditor/net/。如果改动了位置,那么在初始化 UE 的时候也应该配置 serverUrl 值。
这是一个完整的 VS 项目,可以单独部署为一个网站。其中:
net/config.json 服务端配置文件
net/controller.ashx 文件上传入口
net/App_Code/CrawlerHandler.cs 远程抓图动作
net/App_Code/ListFileManager.cs 文件管理动作
net/App_Code/UploadHandler.cs 上传动作
该目录不需要转换为应用程序。
服务端配置
根据 config.json 中 *PathFormat 的默认配置,一般地,上传的图片会保存在 controller.ashx 文件所在目录(即本例中的 /libs/ueditor/)的 upload 目录中:
/libs/ueditor/upload/image/
原因是 UploadHandler.cs 中 Server.MapPath 的参数是由 *PathFormat 决定的。
以修改 config.json 中的 imagePathFormat 为例:
原值:"imagePathFormat": "upload/image/{yyyy}{mm}{dd}/{time}{rand:6}"
改为:"imagePathFormat": "/upload/ueditor/{yyyy}{mm}{dd}/{time}{rand:6}"
以“/”开始的路径在 Server.MapPath 时会定位到网站根目录。
此处不能以“~/”开始,因为最终在客户端显示的图片路径是 imageUrlPrefix + imagePathFormat,若其中包含符号“~”就无法正确显示。
在该配置文件中查找所有 PathFormat,按相同的规则修改。
说到客户端的图片路径,我们只要将
原值:"imageUrlPrefix": "/ueditor/net/"
改为:"imageUrlPrefix": ""
即可返回客户端正确的 URL。
当然也要同步修改 scrawlUrlPrefix、snapscreenUrlPrefix、catcherUrlPrefix、videoUrlPrefix、fileUrlPrefix。
特殊情况,在复制包含图片的网页内容的操作中,若图片地址带“?”等符号,会出现无法保存到磁盘的情况,需要修改以下代码:
打开 CrawlerHandler.cs 文件,找到
ServerUrl = PathFormatter.Format(Path.GetFileName(this.SourceUrl), Config.GetString("catcherPathFormat"));替换成:
ServerUrl = PathFormatter.Format(Path.GetFileName(SourceUrl.Contains("?") ? SourceUrl.Substring(0, SourceUrl.IndexOf("?")) : SourceUrl), Config.GetString("catcherPathFormat"));如果你将图片保存到第三方图库,那么 imageUrlPrefix 值设为相应的域名即可,如:
改为:"imageUrlPrefix": "//cdn.***.com"
然后在 UploadHandler.cs 文件(用于文件上传)中找到
File.WriteAllBytes(localPath, uploadFileBytes);在其下方插入上传到第三方图库的代码,以阿里云 OSS 为例:
// 上传到 OSS
client.PutObject(bucketName, savePath.Substring(1), localPath);在 CrawlerHandler.cs 文件(无程抓图上传)中找到
File.WriteAllBytes(savePath, bytes);在其下方插入上传到第三方图库的代码,以阿里云 OSS 为例:
// 上传到 OSS
client.PutObject(bucketName, ServerUrl.Substring(1), savePath);最后有还有两个以 UrlPrefix 结尾的参数名 imageManagerUrlPrefix 和 fileManagerUrlPrefix 分别是用来列出上传目录中的图片和文件的,
对应的操作是在编辑器上的“多图上传”功能的“在线管理”,和“附件”功能的“在线附件”。
最终列出的图片路径是由 imageManagerUrlPrefix + imageManagerListPath + 图片 URL 组成的,那么:
"imageManagerListPath": "/upload/ueditor/image",
"imageManagerUrlPrefix": "",
以及:
"fileManagerListPath": "/upload/ueditor/file",
"fileManagerUrlPrefix": "",
即可。
如果是上传到第三方图库的,且图库上的文件与本地副本是一致的,那么将 imageManagerUrlPrefix 和 fileManagerUrlPrefix 设置为图库域名,
服务端仍然以 imageManagerListPath 指定的路径来查找本地文件(非图库),但客户端显示图库的文件 URL。
因此,如果文件仅存放在图库上,本地没有副本的情况就无法使用该功能了。
综上,所有的 *UrlPrefix 应该设为一致。
另外记得配置不希望被远程抓图的域名,参数 catcherLocalDomain。
服务端授权
现在来判断一下只有登录用户才允许上传。
首先打开服务端的统一入口文件 controller.ashx,
继承类“IHttpHandler”改为“IHttpHandler, System.Web.SessionState.IRequiresSessionState”,即同时继承两个类,以便可使用 Session,
找到“switch”,其上插入:
if (用户未登录) { throw new System.Exception("请登录后再试"); }即用户已登录或 action 为获取 config 才进入 switch。然后,
else
{
action = new NotAllowedHandler(context);
}这里的 NotAllowedHandler 是参照 NotSupportedHandler 创建的,提示语 state 可以是“登录后才能进行此操作。”
上传目录权限设置
上传目录(即本例中的 /upload/ueditor/ 目录)应设置允许写入和禁止执行。
基本用法
设置内容:
ue.setContent("Hello world.");获取内容:
var a = ue.getContent();更多用法见官方文档:http://fex.baidu.com/ueditor/#api-common
其它事宜
配置上传附件的文件格式
找到文件:config.json,更改“上传文件配置”的 fileAllowFiles 项,
同时在 Web 服务器上允许这些格式的文件可访问权限。以 IIS 为例,在“MIME 类型”模块中添加扩展名。
遇到从客户端(......)中检测到有潜在危险的 Request.Form 值。请参考此文
另外,对于不支持上传 .webp 类型的图片的问题,可以作以下修改:
config.json 中搜索“".bmp"”,替换为“".bmp", ".webp"”
IIS 中选中对应网站或直接选中服务器名,打开“MIME 类型”,添加,文件扩展名为“.webp”,MIME 类型为“image/webp”
最后,为了在内容展示页面看到跟编辑器中相同的效果,请参照官方文档引用 uParse
若有插入代码,再引用:
<link href="/lib/ueditor/utf8-net/third-party/SyntaxHighlighter/shCoreDefault.css" rel="stylesheet" />
<script src="/lib/ueditor/utf8-net/third-party/SyntaxHighlighter/shCore.js"></script>
其它插件雷同。
若对编辑器的尺寸有要求,在初始化时设置即可:
var ue = UE.getEditor('tb_content', {
initialFrameWidth: '100%',
initialFrameHeight: 320
});
本文适用于 IIS 7, IIS 7.5, IIS 8, IIS 8.5, IIS 10 等 Web 服务器,IIS 6(Windows Server 2003)用户请查阅 ISAPI_Rewrite。
在 IIS 中要实现 URL 重写,需要下载并安装 URL Rewrite 组件,http://www.iis.net/downloads/microsoft/url-rewrite
在 IIS 管理器中选中任意网站,主窗口可见“URL 重写”,双击打开。(如果你想配置这台服务器的所有网站有效,直接选中左侧菜单中的服务器名,打开“URL 重写”即可。)
右侧“添加规则...”,选择“入站规则”中的“空白规则”,确定。
填写规则名称,在“匹配 URL”框中选择“与模式匹配”,根据自己的需求选择“正则表达式”、“通配符”或“完全匹配”,“模式”中填写要防盗链的文件路径规则,例如正则表达式 ^.*\.(jpg|png)$ 将匹配所有目录下的 .jpg 和 .png 文件。
接下来将设置图片在允许的域名下显示。
在“条件”框中选择“全部匹配”,点击“添加”,“条件输入”中填写“{HTTP_REFERER}”(不含引号,含花括号),表示判断 HTTP 请求中 Header 的 Referer。选择“与模式不匹配”,模式中填写匹配规则,如 ^$ 表示允许 Referer 为空(如直接从浏览器打开的情况),再加一个规则 ^https?://([^/]*\.)?(xoyozo.net|himiao.com)/.*$ 表示允许在 xoyozo.net 和 himiao.com 这两个域名下显示图片。当然如果你有很多域名或需要设置不同的规则,可以继续添加,但最好把访问量大的规则移到前面,从而减少系统匹配次数,提高访问效率。
最后,在“操作”框中设置你想要的处理方式,可以是“重定向”到一张防盗链提醒的图片上(推荐类型临时 307),也可以自定义响应,例如,状态代码(403),子代码(0),原因(Forbidden: Access is denied.),描述(You do not have permission to view this directory or page using the credentials that you supplied.),查看 HTTP 状态代码。
如果你是配置某个网站的“URL 重写”,那么在网站根目录下的 web.config 文件中,<system.webServer /> 节点下可以看到刚刚配置的规则,例如:
<rewrite>
<rules>
<rule name="RequestBlockingRule1" stopProcessing="true">
<match url="^.*\.(jpg|png)$" />
<conditions>
<add input="{HTTP_REFERER}" pattern="^https?://([^/]*\.)?(xoyozo.net|himiao.com)/.*$" negate="true" />
<add input="{HTTP_REFERER}" pattern="^$" negate="true" />
</conditions>
<action type="Redirect" url="http://42.96.165.253/logo2013.png" redirectType="Temporary" />
</rule>
</rules>
</rewrite>
| 软件名称 | 价格 | 软件介绍 |
|---|---|---|
| ProPresenter | 试用 / $399 | 一款跨平台(Mac、Windows),专为高品质现场(包括晚会、体育赛事、会议等)打造字幕及多媒体展示的软件。 (试用版是全功能的,但输出窗口有水印,试用期两周) |
| Sports Sounds Pro | 免费 / $149.95 | 一款专业用于现场事件的音控软件。 (免费版是全功能的,仅有一些限制,比如:只能播放 10 组中每组的前 3 页的第 1 行,而且只能放置 180 个按钮) |
| Miro Video Converter | 免费 | 可以导出兼容 HTML5 网页播放的视频格式(.mp4)。 |
| Vistumbler | 免费 | 无线网络扫描工具。 |
| VNC | 免费 / $30 / $40 | Mac 上优秀的远程桌面软件。 |
| 免费 | 快速扫描目录大小和空间占用 | |
| IconWorkshop | 试用 / 购买 | 优秀的 ICO、ICON 制作软件,专业图标制作,编辑,转换工具 |
| $19 / $59 | 功能强大的数字音乐编辑器,是一个集声音编辑、播放、录制和转换的音频工具。 | |
| EasyRecovery | EasyRecovery 是由全球著名数据厂商 Kroll Ontrack 出品的一款数据文件恢复软件。支持恢复不同存储介质数据:硬盘、光盘、U盘、移动硬盘、数码相机、手机、Raid 文件恢复等,能恢复包括文档、表格、图片、音视频等各种文件。 | |
| DiskGenius | 一款专业级的数据恢复软件,算法精湛、功能强大!支持多种情况下的文件丢失、分区丢失恢复;支持文件预览;支持扇区编辑、RAID 恢复等高级数据恢复功能。 | |
| sagethumbs | 免费 | 预览 PSD 文件 |
| WebP Codec for Windows | 免费 | 预览 WebP 文件 |
| ventoy | 免费 | 多系统启动U盘解决方案 |
| 普通订阅号 | 认证订阅号 | 普通服务号 | 认证服务号 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 注册主体为个人类型 | √ | × | × | × |
| 注册主体为企业类型(个体工商户,无对公账户) | × | √ | × | √(不能申请微信支付?) |
| 注册主体为企业类型(个体工商户,有对公账户) | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| 注册主体为企业类型(企业公司类) | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| 群发 | 每天 1 条 | 每天 1 条 | 每月 4 条 | 每月 4 条 |
| 接口权限 | 参:https://mp.weixin.qq.com/wiki?t=resource/res_main&id=mp1433401084 | |||
参考资料
http://kf.qq.com/faq/120911VrYVrA130619v6zaAn.html
打开 Fiddler Web Debugger 菜单栏上的 Tools - Fiddler Options...
切换到 HTTPS 选项卡
勾选 Capture HTTPS CONNECTs 及 Decrypt HTTPS traffic,OK
另,这种情况如何破?
*** FIDDLER: RawDisplay truncated at 128 characters. Right-click to disable truncation. ***
最近有服务器不时出现的CPU使用率超高,内存几乎被吃光,系统甚至自动kill掉一些进程,如sshd,vsftpd等。用top查看,PHP-CGI进程高挂不下,如下是解决方案:
一、进程跟踪
# top //找出CPU使用率高的进程PID
# strace -p PID //跟踪进程
# ll /proc/PID/fd //查看该进程在处理哪些文件
将有可疑的PHP代码修改之,如:file_get_contents没有设置超时时间。
二、内存分配
如果进程跟踪无法找到问题所在,再从系统方面找原因,会不会有可能内存不够用?据说一个较为干净的PHP-CGI打开大概20M-30M左右的内存,决定于PHP模块开启多少。
通过pmap指令查看PHP-CGI进程的内存使用情况
# pmap $(pgrep php-cgi |head -1)
按输出的结果,结合系统的内存大小,配置PHP-CGI的进程数(max_children)。
三、监控
最后,还可以通过监控与自动恢复的脚本保证服务的正常运转。下面是我用到的一些脚本:
只要一个php-cgi进程占用的内存超过 %1 就把它kill掉
#!/bin/sh
PIDS=`ps aux|grep php-cgi|grep -v grep|awk’{if($4>=1)print $2}’`
for PID in $PIDS
do
echo `date +%F….%T`>>/data/logs/phpkill.log
echo $PID >> /data/logs/phpkill.log
kill -9 $PID
done
检测php-fpm进程
#!/bin/bash
netstat -tnlp | grep “php-cgi” >> /dev/null #2&> /data/logs/php_fasle.log
if [ "$?" -eq "1" ];then #&& [ `netstat -tnlp | grep 9000 | awk '{ print $4}' | awk -F ":" '{print $2}'` -eq "1" ];then
/usr/local/webserver/php/sbin/php-fpm start
echo `date +%F….%T` “System memory OOM.Kill php-cgi. php-fpm service start. ” >> /data/logs/php_monitor.log
fi
通过http检测php执行
#!/bin/bash
status=`curl -s –head “http://127.0.0.1:8080/chk.php” | awk ‘/HTTP/ {print $2}’`
if [ $status != "200" -a $status != "304" ]; then
/usr/local/webserver/php/sbin/php-fpm restart
echo `date +%F….%T` “php-fpm service restart” >> /data/logs/php_monitor.log
fi

编者按:今天腾讯万技师同学的这篇技术总结必须强烈安利下,目录清晰,层次分明,每个接口都有对应的简介、系统要求、实例、核心代码以及超实用的思维发散,帮你直观把这些知识点get起来。以现在HTML 5的势头,同志们,你看到的这些,可都是钱呐。
十二年前,无论多么复杂的布局,在我们神奇的table面前,都不是问题;
十年前,阿捷的一本《网站重构》,为我们开启了新的篇章;
八年前,我们研究yahoo.com,惊叹它在IE5下都表现得如此完美;
六年前,Web标准化成了我们的基础技能,我们开始研究网站性能优化;
四年前,我们开始研究自动化工具,自动化测试,谁没玩过nodejs都不好意思说是页面仔;
二年前,各种终端风起云涌,响应式、APP开发都成为了我们研究的范围,CSS3动画开始风靡;
如今,CSS3动画、Canvas、SVG、甚至webGL你已经非常熟悉,你是否开始探寻,接下来,我们可以玩什么,来为我们项目带来一丝新意?
没错,本文就是以HTML5 Device API为核心,对HTML5的一些新接口作了一个完整的测试,希望能让大家有所启发。
目录:
一、让音乐随心而动 – 音频处理 Web audio API
二、捕捉用户摄像头 – 媒体流 Media Capture
三、你是逗逼? – 语音识别 Web Speech API
四、让我尽情呵护你 – 设备电量 Battery API
五、获取用户位置 – 地理位置 Geolocation API
六、把用户捧在手心 – 环境光 Ambient Light API
七、陀螺仪 Deviceorientation
八、Websocket
九、NFC
十、震动 - Vibration API
十一、网络环境 Connection API
一、让音乐随心而动 – 音频处理 Web audio API
简介:
Audio对象提供的只是音频文件的播放,而Web Audio则是给了开发者对音频数据进行分析、处理的能力,比如混音、过滤。
系统要求:
ios6+、android chrome、android firefox
实例:

http://sy.qq.com/brucewan/device-api/web-audio.html
核心代码:
var context = new webkitAudioContext();
var source = context.createBufferSource(); // 创建一个声音源
source.buffer = buffer; // 告诉该源播放何物
createBufferSourcesource.connect(context.destination); // 将该源与硬件相连
source.start(0); //播放
技术分析:
当我们加载完音频数据后,我们将创建一个全局的AudioContext对象来对音频进行处理,AudioContext可以创建各种不同功能类型的音频节点AudioNode,比如

1、源节点(source node)
我们可以使用两种方式加载音频数据:
<1>、audio标签
var sound, audio = new Audio();
audio.addEventListener('canplay', function() {
sound = context.createMediaElementSource(audio);
sound.connect(context.destination);
});
audio.src = '/audio.mp3';
<2>、XMLHttpRequest
var sound, context = createAudioContext();
var audioURl = '/audio.mp3'; // 音频文件URL
var xhr = new XMLHttpRequest();
xhr.open('GET', audioURL, true);
xhr.responseType = 'arraybuffer';
xhr.onload = function() {
context.decodeAudioData(request.response, function (buffer) {
source = context.createBufferSource();
source.buffer = buffer;
source.connect(context.destination);
}
}
xhr.send();
2、分析节点(analyser node)
我们可以使用AnalyserNode来对音谱进行分析,例如:
var audioCtx = new (window.AudioContext || window.webkitAudioContext)();
var analyser = audioCtx.createAnalyser();
analyser.fftSize = 2048;
var bufferLength = analyser.frequencyBinCount;
var dataArray = new Uint8Array(bufferLength);
analyser.getByteTimeDomainData(dataArray);
function draw() {
drawVisual = requestAnimationFrame(draw);
analyser.getByteTimeDomainData(dataArray);
// 将dataArray数据以canvas方式渲染出来
};
draw();
3、处理节点(gain node、panner node、wave shaper node、delay node、convolver node等)
不同的处理节点有不同的作用,比如使用BiquadFilterNode调整音色(大量滤波器)、使用ChannelSplitterNode分割左右声道、使用GainNode调整增益值实现音乐淡入淡出等等。
需要了解更多的音频节点可能参考:
https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/API/Web_Audio_API
4、目的节点(destination node)
所有被渲染音频流到达的最终地点
思维发散:
1、可以让CSS3动画跟随背景音乐舞动,可以为我们的网页增色不少;
2、可以尝试制作H5酷酷的变声应用,增加与用户的互动;
3、甚至可以尝试H5音乐创作。
看看google的创意:http://v.youku.com/v_show/id_XNTk0MjQyNDMy.html
二、捕捉用户摄像头 – 媒体流 Media Capture
简介:
通过getUserMedia捕捉用户摄像头获取视频流和通过麦克风获取用户声音。
系统要求:
android chrome、android firefox
实例:
捕获用户摄像头 捕获用户麦克风

http://sy.qq.com/brucewan/device-api/camera.html

http://sy.qq.com/brucewan/device-api/microphone-usermedia.html
核心代码:
1、摄像头捕捉
navigator.webkitGetUserMedia ({video: true}, function(stream) {
video.src = window.URL.createObjectURL(stream);
localMediaStream = stream;
}, function(e){
})
2、从视频流中拍照
btnCapture.addEventListener('touchend', function(){
if (localMediaStream) {
canvas.setAttribute('width', video.videoWidth);
canvas.setAttribute('height', video.videoHeight);
ctx.drawImage(video, 0, 0);
}
}, false);
3、用户声音录制
navigator.getUserMedia({audio:true}, function(e) {
context = new audioContext();
audioInput = context.createMediaStreamSource(e);
volume = context.createGain();
recorder = context.createScriptProcessor(2048, 2, 2);
recorder.onaudioprocess = function(e){
recordingLength += 2048;
recorder.connect (context.destination);
}
}, function(error){});
4、保存用户录制的声音
var buffer = new ArrayBuffer(44 + interleaved.length * 2);
var view = new DataView(buffer);
fileReader.readAsDataURL(blob); // android chrome audio不支持blob
… audio.src = event.target.result;
思维发散:
1、从视频拍照自定义头像;
2、H5视频聊天;
3、结合canvas完成好玩的照片合成及处理;
4、结合Web Audio制作有意思变声应用。
三、你是逗逼? – 语音识别 Web Speech API简介:
1、将文本转换成语音;
2、将语音识别为文本。
系统要求:
ios7+,android chrome,android firefox
测试实例:

http://sy.qq.com/brucewan/device-api/microphone-webspeech.html
核心代码:
1、文本转换成语音,使用SpeechSynthesisUtterance对象;
var msg = new SpeechSynthesisUtterance();
var voices = window.speechSynthesis.getVoices();
msg.volume = 1; // 0 to 1
msg.text = ‘识别的文本内容’;
msg.lang = 'en-US';
speechSynthesis.speak(msg);
2、语音转换为文本,使用SpeechRecognition对象。
var newRecognition = new webkitSpeechRecognition();
newRecognition.onresult = function(event){
var interim_transcript = '';
for (var i = event.resultIndex; i < event.results.length; ++i) {
final_transcript += event.results[i][0].transcript;
}
};
测试结论:
1、Android支持不稳定;语音识别测试失败(暂且认为是某些内置接口被墙所致)。
思维发散:
1、当语音识别成为可能,那声音控制将可以展示其强大的功能。在某些场景,比如开车、网络电视,声音控制将大大改善用户体验;
2、H5游戏中最终分数播报,股票信息实时声音提示,Web Speech都可以大放异彩。
四、让我尽情呵护你 – 设备电量 Battery API简介:
查询用户设备电量及是否正在充电。
系统要求:
android firefox
测试实例:

http://sy.qq.com/brucewan/device-api/battery.html
核心代码:
var battery = navigator.battery || navigator.webkitBattery || navigator.mozBattery || navigator.msBattery;
var str = '';
if (battery) {
str += '<p>你的浏览器支持HTML5 Battery API</p>';
if(battery.charging) {
str += '<p>你的设备正在充电</p>';
} else {
str += '<p>你的设备未处于充电状态</p>';
}
str += '<p>你的设备剩余'+ parseInt(battery.level*100)+'%的电量</p>';
} else {
str += '<p>你的浏览器不支持HTML5 Battery API</p>';
}
测试结论:
1、QQ浏览器与UC浏览器支持该接口,但未正确显示设备电池信息;
2、caniuse显示android chrome42支持该接口,实测不支持。
思维发散:
相对而言,我觉得这个接口有些鸡肋。
很显然,并不合适用HTML5做电池管理方面的工作,它所提供的权限也很有限。
我们只能尝试做一些优化用户体验的工作,当用户设备电量不足时,进入省电模式,比如停用滤镜、摄像头开启、webGL、减少网络请求等。
五、获取用户位置 – 地理位置 Geolocation简介:
Geolocation API用于将用户当前地理位置信息共享给信任的站点,目前主流移动设备都能够支持。
系统要求:
ios6+、android2.3+
测试实例:

http://sy.qq.com/brucewan/device-api/geolocation.html
核心代码:
var domInfo = $("#info");
// 获取位置坐标
if (navigator.geolocation) {
navigator.geolocation.getCurrentPosition(showPosition,showError);
}
else{
domInfo.innerHTML="抱歉,你的浏览器不支持地理定位!";
}
// 使用腾讯地图显示位置
function showPosition(position) {
var lat=position.coords.latitude;
var lon=position.coords.longitude;
mapholder = $('#mapholder')
mapholder.style.height='250px';
mapholder.style.width = document.documentElement.clientWidth + 'px';
var center = new soso.maps.LatLng(lat, lon);
var map = new soso.maps.Map(mapholder,{
center: center,
zoomLevel: 13
});
var geolocation = new soso.maps.Geolocation();
var marker = null;
geolocation.position({}, function(results, status) {
console.log(results);
var city = $("#info");
if (status == soso.maps.GeolocationStatus.OK) {
map.setCenter(results.latLng);
domInfo.innerHTML = '你当前所在城市: ' + results.name;
if (marker != null) {
marker.setMap(null);
}
// 设置标记
marker = new soso.maps.Marker({
map: map,
position:results.latLng
});
} else {
alert("检索没有结果,原因: " + status);
}
});
}
测试结论:
1、Geolocation API的位置信息来源包括GPS、IP地址、RFID、WIFI和蓝牙的MAC地址、以及GSM/CDMS的ID等等。规范中没有规定使用这些设备的先后顺序。
2、初测3g环境下比wifi环境理定位更准确;
3、测试三星 GT-S6358(android2.3) geolocation存在,但显示位置信息不可用POSITION_UNAVAILABLE。
六、把用户捧在手心 – 环境光 Ambient Light简介:
Ambient Light API定义了一些事件,这些时间可以提供源于周围光亮程度的信息,这通常是由设备的光感应器来测量的。设备的光感应器会提取出辉度信息。
系统要求:
android firefox
测试实例:

http://sy.qq.com/brucewan/device-api/ambient-light.html
核心代码:
这段代码实现感应用前当前环境光强度,调整网页背景和文字颜色。
var domInfo = $('#info');
if (!('ondevicelight' in window)) {
domInfo.innerHTML = '你的设备不支持环境光Ambient Light API';
} else {
var lightValue = document.getElementById('dl-value');
window.addEventListener('devicelight', function(event) {
domInfo.innerHTML = '当前环境光线强度为:' + Math.round(event.value) + 'lux';
var backgroundColor = 'rgba(0,0,0,'+(1-event.value/100) +')';
document.body.style.backgroundColor = backgroundColor;
if(event.value < 50) {
document.body.style.color = '#fff'
} else {
document.body.style.color = '#000'
}
});
}
思维发散:
该接口适合的范围很窄,却能做出很贴心的用户体验。
1、当我们根据Ambient Light强度、陀螺仪信息、当地时间判断出用户正躺在床上准备入睡前在体验我们的产品,我们自然可以调整我们背景与文字颜色让用户感觉到舒适,我们还可以来一段安静的音乐,甚至使用Web Speech API播报当前时间,并说一声“晚安”,何其温馨;
2、该接口也可以应用于H5游戏场景,比如日落时分,我们可以在游戏中使用安静祥和的游戏场景;
3、当用户在工作时间将手机放在暗处,偷偷地瞄一眼股市行情的时候,我们可以用语音大声播报,“亲爱的,不用担心,你的股票中国中车马上就要跌停了”,多美的画面。
参考文献:
https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/API
http://webaudiodemos.appspot.com/
http://www.w3.org/2009/dap/
去年,我们分享了《40个良好用户界面Tips》,对设计师来说确实很有帮助,今年,Goodui.org已经更新至71条,这些原则都是由Goodui官方精心整理,认为这些都是非常重要的设计要点,所以对于设计师来说,建议学习一下。
01 尝试使用一列的布局替代多列布局

02 给用户一些小的利益,别看上去那么赤裸裸
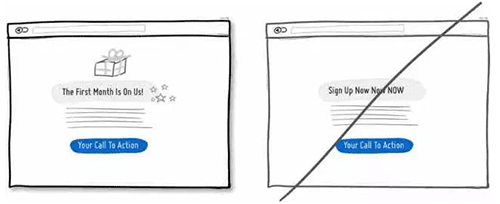
03 合并相似的功能

04 尝试展示来自用户的赞扬,而不是自我表扬

05 重复核心行动点

06 统一视觉规范,提升可识别性

07 尝试使用推荐的口吻,而不是让用户感觉面对一台冷冰冰的机器
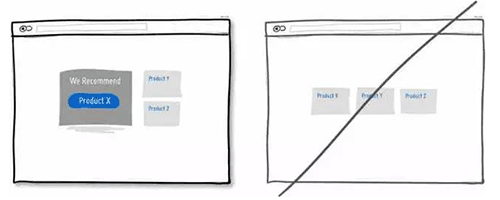
08 给用户吃「后悔药」的机会
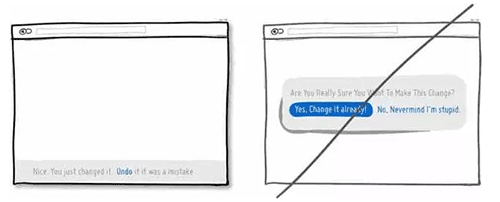
09 告诉用户产品适用的人群,而不是人人都通用

10 将文案写得更加的直接,而不是一堆废话
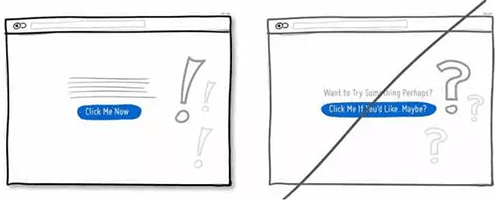
11 增强主行动点的视觉冲击力,提升它在页面中的可对比性
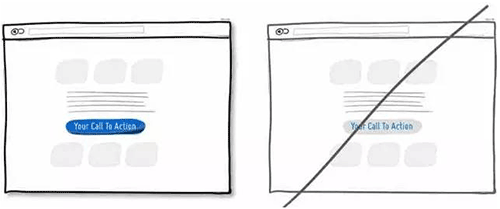
12 让用户知道你从哪儿来更易于拉近与用户的关系
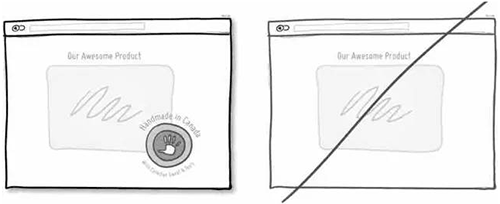
13 将表单做的简单点,确保用户在抓狂之前能进入下一步

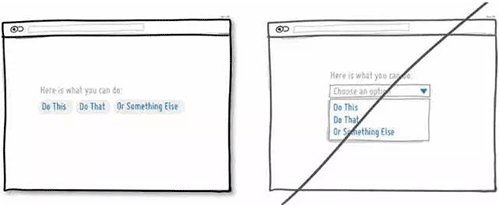
14 尽量将用户需要选择的信息展示出来而不是藏起来
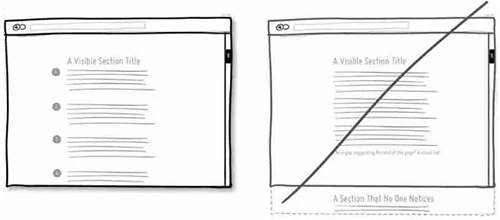
15 页面的排版需要考虑用户是否会漏掉底部信息
16 如果页面的底部有需要关注的行动点,别让文中过多的外链带走了用户

17 确保用户知道自己目前的状态

18 将利益点融合在行动点中,增强用户的点击欲望
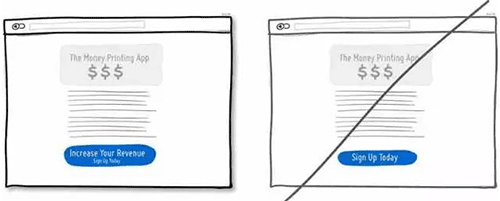
19 将行动点与当前信息结合起来

20 将简要的表单合并到页面中,减少调整页面带来的用户流失

21 适当的增加延迟动效,让用户感知到页面的变化
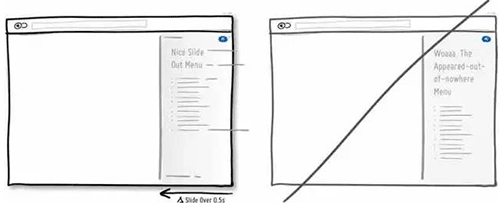
22 让新用户从尝试产品入手,而不是一来就面对冷冰冰的注册表单
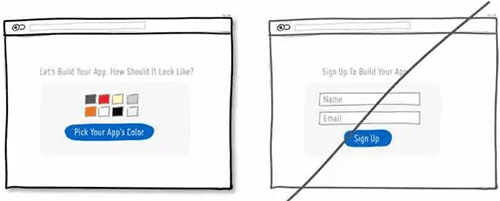
23 减少使用线框,这会过多的吸引用户注意力,而且会让页面看上去透不过气
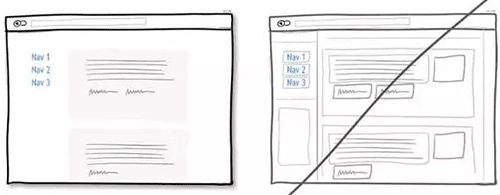
24 给用户推销你能给他带来的利益,而不是功能

25 一定要注意0结果页面的设计,这也是引导用户的好地方
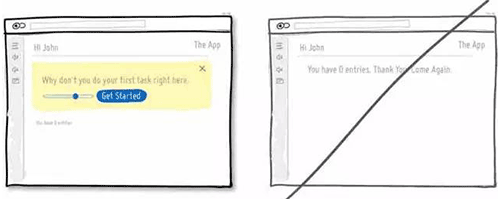
26 给用户选择退出的权利,特别是邮件订阅
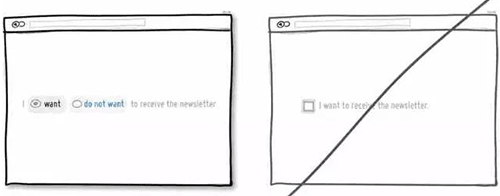
27 注意界面元素的一致性,降低用户学习成本
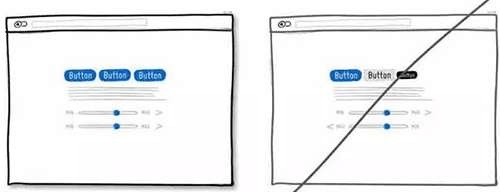
28 给下拉框增加一些预设值,降低用户填写成本
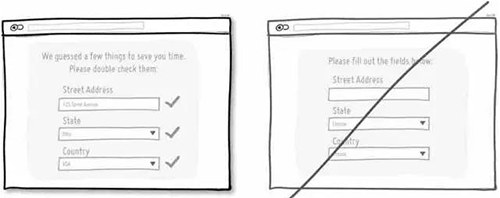
29 延续用户日常的使用习惯,而不是重新创造

30 尝试告诉用做些事情降低自己的损失,而不是提升收益
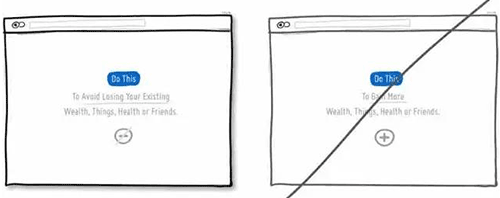
31 提升页面的视觉层次,增强可阅读性
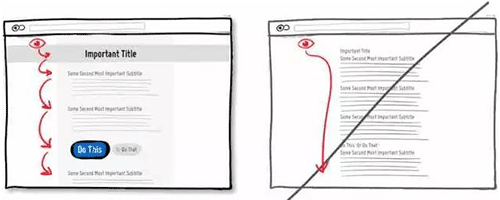
32 将同类的操作合并在一起,降低用户的认知成本
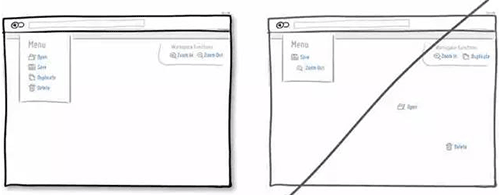
33 表单及时校验,而不是统一提交后在告诉用户填错了

34 尝试将表单输入变得更加宽容,让用户的填写更加简单
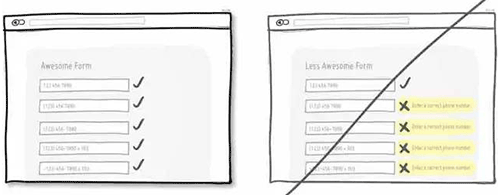
35 通过时间增强紧迫感
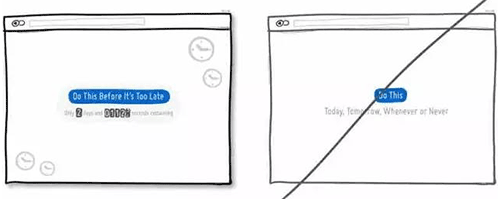
36 提供用户可预见性的操作,降低用户的心理成本
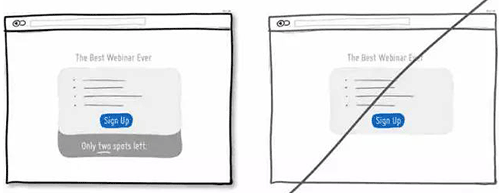
37 尽可能的帮助用户选择,而不是让用户想破脑袋
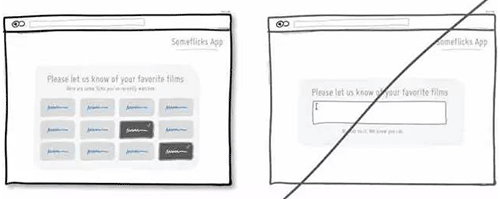
38 尽可能将操作区域放大,降低用户操作成本
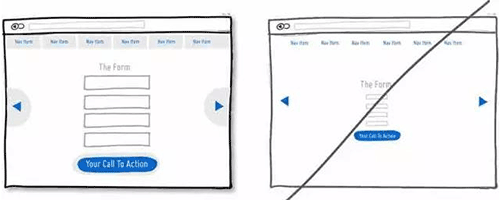
39 页面加载速度很重要,尽可能让用户感受到你的网站速度很快
40 如果可以,增加键盘快捷键,提升操作效率
41 尝试通过对比来让用户感知到性价比
42 尝试对进度条进行「设计」来降低用户等待的焦虑
43 根据用户选择逐步展示信息,降低无效信息对用户的干扰
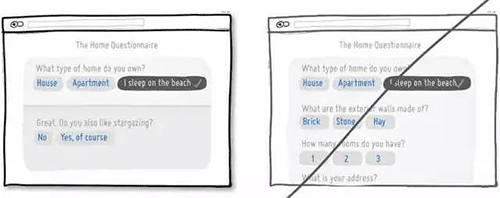
44 有时候较小的承诺比「夸海口」会更容易让用户信服

45 尝试将提示信息弱化,减少对用户操作的干扰
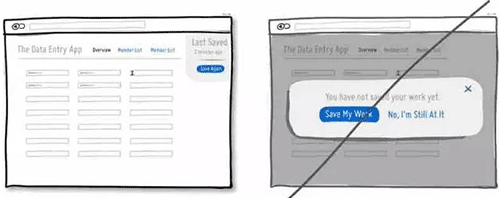
46 尽量通过系统的功能来简化用户的操作
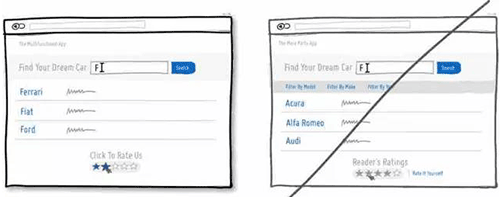
47 用文本配合图标来降低用户的认知成本

48 用更自然的语言代替冷冰冰的机器
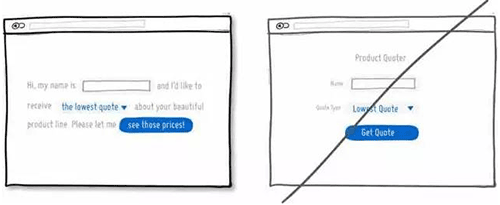
49 放出一些摘要信息来帮助用户识别是否需要进一步了解
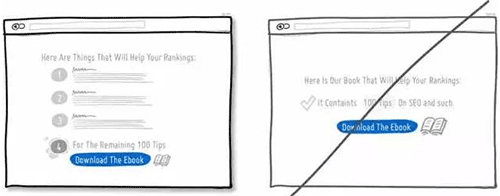
50 在关键的页面增加用户权益信息,增强用户进一步操作的信心
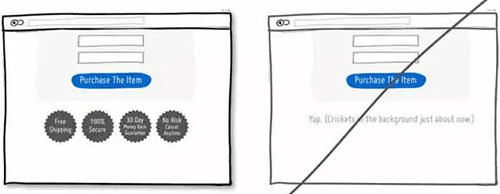
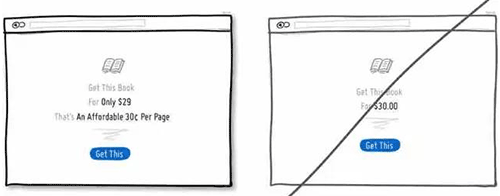
51 将价格进行换算,让用户感觉这很便宜
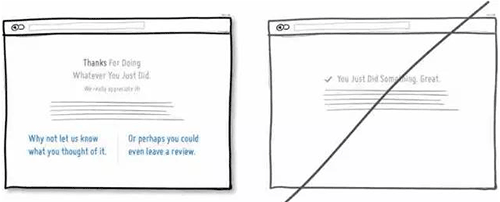
52 记得在成功页面感谢用户
53 将数字转化成易于用户阅读的形式,而不是冷冰冰的机器语言
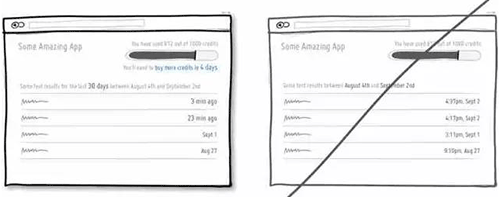
54 告诉用户选择的权利和自由「诱惑力」
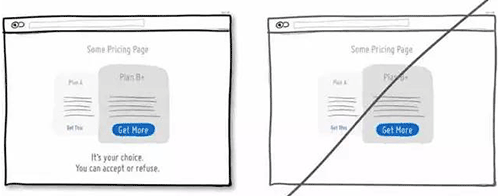
55 尝试让语言更具「诱惑力」
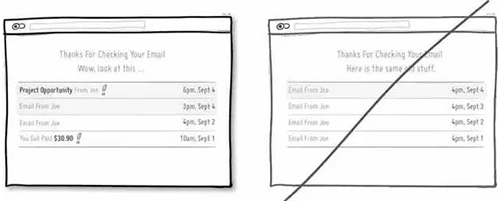
56 通过设计引导用户的注意力
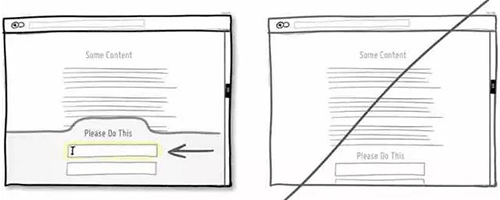
57 通过友好的对比来展示产品,为用户做决定提供帮助

58 通过任务机制来提升用户的满足感
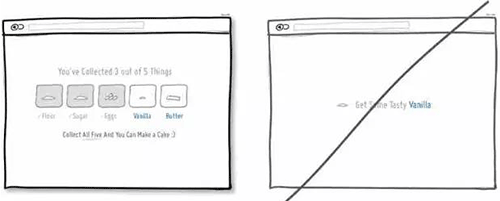
59 让用户了解接下来将要发生什么事情

60 尝试用更幽默一些的语言文案

61 任何操作之后都要给出反馈,让用户知道操作已经生效

62 注意动效的真实使用情况(Amazon 的类目菜单就是一个很好的例子)

63 注意排版的,不要让信息过于拥挤
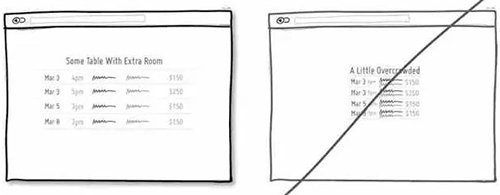
64 尝试用讲故事的方式来传递信息,增强用户的代入感
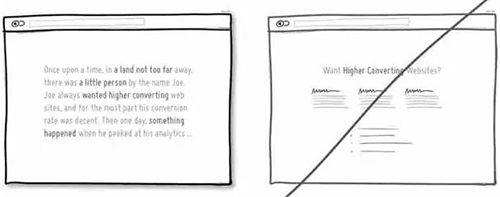
65 尽量给用户展示真实的信息,不要欺骗

66 随着用户的不断熟悉简化界面
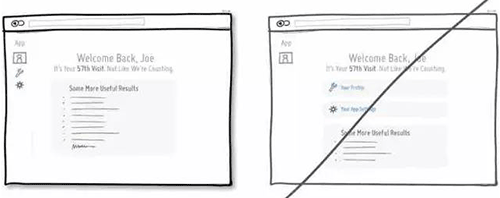
67 试着用用户的口吻展示信息
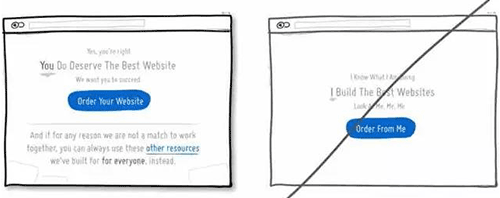
68 在表单中增加一些提示信息,减少错误的几率
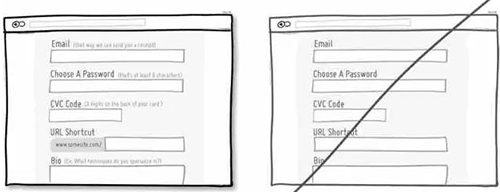
69 用简单的文案传递核心关注的信息,少一些废话

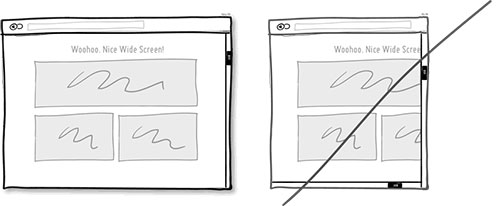
70 尝试使用响应式布局
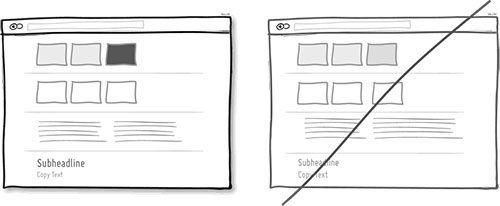
71 视觉表达要清晰,而不是模棱两可
这71条设计原则虽然针对 Web 设计,但有些部分在移动产品设计中同样有效。翻译过程只保留了图片和标题,更多详细内容可以访问 GoodUI 官网:
http://goodui.org/
Apple’s newest devices feature the Retina Display, a screen that packs double as many pixels into the same space as older devices. For designers this immediately brings up the question, “What can I do to make my content look outstanding on these new iPads and iPhones?”. First there are a few tough questions to consider, but then this guide will help you get started making your websites and web apps look amazingly sharp with Retina images!

Things to Consider When Adding Retina Images
The main issue with adding retina images is that the images are double as large and will take up extra bandwidth (this won’t be an issue for actual iOS apps, but this guide is covering web sites & web apps only). If your site is mostly used on-the-go over a 3G network it may not be wise to make all your graphics high-definition, but maybe choose only a select few important images. If you’re creating something that will be used more often on a WI-FI connection or have an application that is deserving of the extra wait for hi-res graphics these steps below will help you target only hi-res capable devices.
Simple Retina Images
The basic concept of a Retina image is that your taking a larger image, with double the amount of pixels that your image will be displayed at (e.g 200 x 200 pixels), and setting the image to fill half of that space (100 x 100 pixels). This can be done manually by setting the height and width in HTML to half the size of your image file.
<img src="my200x200image.jpg" width="100" height="100">
If you’d like to do something more advanced keep reading below for how you can apply this technique using scripting.
Creating Retina Icons for Your Website
When users add your website or web app to their homescreen it will be represented by an icon. These sizes for regular and Retina icons (from Apple) are as follows:
![]()
| iPhone | 57 x 57 |
|---|---|
| Retina iPhone | 114 x 114 |
| iPad | 72 x 72 |
| Retina iPad | 144 x 144 |
For each of these images you create you can link them in the head of your document like this (if you want the device to add the round corners remove -precomposed):
<link href="touch-icon-iphone.png" rel="apple-touch-icon-precomposed" />
<link href="touch-icon-ipad.png" rel="apple-touch-icon-precomposed" sizes="72x72" />
<link href="touch-icon-iphone4.png" rel="apple-touch-icon-precomposed" sizes="114x114" />
<link href="touch-icon-ipad3.png" rel="apple-touch-icon-precomposed" sizes="144x144" />
If the correct size isn’t specified the device will use the smallest icon that is larger than the recommended size (i.e. if you left out the 114px the iPhone 4 would use the 144px icon).
Retina Background Images
Background images that are specified in your CSS can be swapped out using media queries. You’ll first want to generate two versions of each image. For example ‘bgPattern.png’ at 100px x 100px and ‘bgPattern@2x.png’ at 200px x 200px. It will be useful to have a standard naming convention such as adding @2x for these retina images. To add the new @2x image to your site simply add in the media query below (You can add any additional styles that have background images within the braces of the same media query):
.repeatingPattern {
background: url(../images/bgPattern.png) repeat;
background-size: 100px 100px;
}
@media only screen and (-webkit-min-device-pixel-ratio: 2) {
.repeatingPattern {
background: url(../images/bgPattern@2x.png) repeat;
}
}
JavaScript for Retina Image Replacement
For your retina images that aren’t backgrounds the best option seems to be either creating graphics with CSS, using SVG, or replacing your images with JavaScript. Just like the background images, you’ll want to create a normal image and one ‘@2x’ image. Then with JavaScript you can detect if the pixel ratio of the browser is 2x, just like you did with the media query:
if (window.devicePixelRatio == 2) {
//Replace your img src with the new retina image
}
If you’re using jQuery you could quickly replace all your images like this very basic example below. It’s a good idea to add a class to identify the images with hi-res versions so you don’t replace any others by mistake. I’ve added a class=”hires” for this example. Also make sure you have the standard (non-retina) image height and width set in the HTML:
<img class="hires" alt="" src="search.png" width="100" height="100" />
<script type="text/javascript">
$(function () {
if (window.devicePixelRatio == 2) {
var images = $("img.hires");
// loop through the images and make them hi-res
for(var i = 0; i < images.length; i++) {
// create new image name
var imageType = images[i].src.substr(-4);
var imageName = images[i].src.substr(0, images[i].src.length - 4);
imageName += "@2x" + imageType;
//rename image
images[i].src = imageName;
}
}
});
</script>
Server-Side Retina Images
If you’d like to implement a server-side retina image solution, I recommend checking out Jeremy Worboys’ Retina Images (which he also posted in the comments below). His solution uses PHP code to determine which image should be served. The benefit of this solution is that it doesn’t have to replace the small image with the retina one so you’re using less bandwidth, especially if you have lots of images that you’re replacing.
Website Optimization for Retina Displays
If you’re looking for additional information on creating Retina images, I’ve recently had a short book published called Website Optimization for Retina Displays that covers a range of related topics. It contains some of what is above, but also includes samples for many different situations for adding Retina images. It explains the basics of creating Retina images, backgrounds, sprites, and borders. Then it talks about using media queries, creating graphics with CSS, embedding fonts, creating app icons, and more tips for creating Retina websites.
xoyozo 曾经写过 简单实现在 ASP.NET 中执行 URL 重写,文中提到使用微软的 URLRewriter.dll 来配置实现 ASP.NET 的 URL 重写,并以此扩展为任意扩展名及目录的 URL 重写。本文在此基础上再次扩展,使之支持泛域名解析。
首先,您的网站必需放在独立服务器或 VPS 中,虚拟空间可能不支持泛解析。
进入域名控制面板,配置 A 记录:通配符(*)星号解析到网站所在的 IP。
根据前文配置 URL 重写。
<configuration> 节点下配置:
<RewriterConfig> <Rules> <RewriterRule> <LookFor>http://([a-zA-Z0-9-]+)\.域名/</LookFor> <SendTo>~/u.aspx?u=$1</SendTo> </RewriterRule> </Rules> </RewriterConfig>
