收录了一些个人觉得不错的网页开发插件。
由于插件更新频繁,本页如有错误请指正,也欢迎告知更多功能强大、使用方便的插件。
| 插件 | 简介 | 备注 |
| 框架 | ||
| jQuery | 最流行的 JS 框架 | 下载、中文文档、英文整合文档、中文整合文档,浏览器支持、来自 css88 的文档 官方建议 IE 6-8 使用 1.12.4 |
| Angular、中文版 AngularJS (version 1.x) | 一套框架,多种平台同时适用手机与桌面 | MVC 架构,使得开发现代的单一页面应用程序(SPAs:Single Page Applications)变得更加容易 |
| Vue.js | 是一套用于构建用户界面的渐进式框架。 | |
| Bootstrap、中文版 | 简洁、直观、强悍的前端开发框架 | 英文文档、v3中文文档、v2中文文档、视频教程,主题和模板 |
| jQuery UI | 为 jQuery 提供更丰富的功能 | 示例:Datepicker、Color Animation、Shake Effect |
| 功能 | ||
| jQuery File Upload | jQuery 文件上传 | 英文文档 |
| jQuery Cookie | 读取、写入和删除 cookie | 浏览器支持,文档 |
| json2.js | json 操作库 | 已弃用,旧 IE 用 jQuery 的 parseJSON,HTML 5 用 JSON.parse |
| Lightbox | 老牌图片浏览插件 推荐使用更强大的 Viewer.js | |
| Swiper、中文版 | 最现代的移动触摸滑块(Most Modern Mobile Touch Slider) | 英文文档,中文文档,旧浏览器支持版本:2.x.x,Swiper 2 英文文档,中文文档 |
| jquery-cropper | 图片裁剪 | |
| FastClick | 用于消除手机浏览器上触摸事件触发之间的 300 毫秒延迟 | 用法,不应用的场景 |
| PACE | 页面加载进度条 | 文档,IE8+ |
| toastr | jQuery 通知 | 文档 |
| Autosize | 一款小巧的,可自动调整 textarea 高度的独立脚本 | IE9+ |
| X-editable | 允许您在页面上创建可编辑元素 | 文档,Demo |
| select2 | 一款提供搜索过滤、自定义样式的下拉框插件 | |
| jQuery Tags Input | 标签输入框 | 用法 |
| Viewer.js | 图片浏览插件 | GitHub(viewerjs)、GitHub(jquery-viewer) jquery-viewer 是 viewerjs 的 jQuery 插件,即在 jQuery 环境中要同时引用这两个脚本。 |
| PDF.js | A general-purpose, web standards-based platform for parsing and rendering PDFs. | |
| 编辑器 | ||
| UEditor | 百度在线编辑器 | GitHub 下载、文档、ASP.NET 部署教程 |
| 日期时间 | ||
| bootstrap-datepicker | Bootstrap 日期选择器 | Online Demo |
| DateTimePicker | 日期时间选择 | |
| MultiDatesPicker | 多日期选择 | |
| FullCalendar | 日历日程事件工作表 | IE 9+, jQuery 2.0.0+ |
| TimeTo | 计时、倒计时 | |
| 图表 | ||
| D3.js | D3.js 是基于数据驱动文档工作方式的一款 JavaScript 函数库,主要用于网页作图、生成互动图形,是最流行的可视化库之一。 | |
| Highcharts、中文版 | 兼容 IE6+、完美支持移动端、图表类型丰富、方便快捷的 HTML5 交互性图表库 | 文档 |
| ECharts | 百度图表控件 | |
| AntV | 来自蚂蚁金服的专业、简单、无限可能的可视化解决方案 G2 - 专业易用的可视化类库 G2-mobile - 移动端高性能可视化类库 G6 - 关系图可视化类库 | 流程图, 关系图, 可视化规范, 地图, 河流图, 力导图, 网络图, UML图, 业务流程图, 时序图 |
| SyntaxHighlighter | 功能齐全的代码语法高亮插件(JS) | |
| 动态排名数据可视化 | 将历史数据排名转化为动态柱状图图表 开源代码,非插件,修改使用 | GitHub、视频教程、EV录屏、网页示例、视频效果 |
| 图标 | ||
| Font Awesome | 完美的图标字体 | IE 8+,v3.2.1 支持 IE 7,进阶用法(定宽/边框/动画/旋转/叠加) |
| Glyphicons | 图标字体 | 作为 Bootstrap 组件 |
| Iconfont | 阿里巴巴矢量图标库 | 用户可以自定义下载多种格式的 icon,也可将图标转换为字体,便于前端工程师自由调整与调用 |
| UI 框架 | ||
| WeUI | 同微信原生视觉体验一致的基础样式库 | Demo、Wiki |
| Apple UI Design Resources | 苹果用户界面设计资源 | |
将字符串作为文本文档输出:
Response.AddHeader("Content-Disposition", "attachment; filename=文件名.txt");
Response.Write(字符串内容);
Response.End();
直接提供服务器文件下载:
FileInfo thefile = new FileInfo(path);
Response.Clear();
Response.ClearHeaders();
Response.Buffer = false;
Response.ContentType = "application/octet-stream";
Response.AppendHeader("Content-Disposition", "attachment;filename=" + HttpUtility.UrlEncode("刮刮卡参与") + id + ".csv");
Response.AppendHeader("Content-Length", thefile.Length.ToString());
Response.WriteFile(thefile.FullName);
Response.Flush();
Response.End();
输出使用 NPOI 创建的 Excel(MemoryStream):
HSSFWorkbook book = new HSSFWorkbook();
……
MemoryStream ms = new MemoryStream();
book.Write(ms);
Response.AddHeader("Content-Disposition", string.Format("attachment; filename={0}.xls", scene.d.drama + " " + scene.s.time_show.ToString("yyyy年MM月dd日HH时mm分")));
Response.BinaryWrite(ms.ToArray());
Response.End();
book = null;
ms.Close();
ms.Dispose();
最后,如果要指定文件编码,加上这句就行:
Response.ContentEncoding = Encoding.xxx;
Repeater
索引 <%# Container.ItemIndex %>
输出项 <%# Container.DataItem %> 或 <%# GetDataItem() %>
ListView
索引 <%# Container.DataItemIndex %>
输出项 <%# GetDataItem() %>
以 fiels 的内容为 <span style="color: red;">你好</span> 为例:
| 语法 | HTML 源代码输出结果 | 浏览器展示结果 | 备注 |
| <%# Eval("field") %> | <span style="color: red;">你好</span> | 你好 | 一般绑定 |
| <%#: Eval("field") %> | <span style="color: red;">你好</span> | <span style="color: red;">你好</span> | HtmlEncode 效果绑定 |
前言
最近在学习Web Api框架的时候接触到了async/await,这个特性是.NET 4.5引入的,由于之前对于异步编程不是很了解,所以花费了一些时间学习一下相关的知识,并整理成这篇博客,如果在阅读的过程中发现不对的地方,欢迎大家指正。
同步编程与异步编程
通常情况下,我们写的C#代码就是同步的,运行在同一个线程中,从程序的第一行代码到最后一句代码顺序执行。而异步编程的核心是使用多线程,通过让不同的线程执行不同的任务,实现不同代码的并行运行。
前台线程与后台线程
关于多线程,早在.NET2.0时代,基础类库中就提供了Thread实现。默认情况下,实例化一个Thread创建的是前台线程,只要有前台线程在运行,应用程序的进程就一直处于运行状态,以控制台应用程序为例,在Main方法中实例化一个Thread,这个Main方法就会等待Thread线程执行完毕才退出。而对于后台线程,应用程序将不考虑其是否执行完毕,只要应用程序的主线程和前台线程执行完毕就可以退出,退出后所有的后台线程将被自动终止。来看代码应该更清楚一些:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace ConsoleApp
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine("主线程开始");
//实例化Thread,默认创建前台线程
Thread t1 = new Thread(DoRun1);
t1.Start();
//可以通过修改Thread的IsBackground,将其变为后台线程
Thread t2 = new Thread(DoRun2) { IsBackground = true };
t2.Start();
Console.WriteLine("主线程结束");
}
static void DoRun1()
{
Thread.Sleep(500);
Console.WriteLine("这是前台线程调用");
}
static void DoRun2()
{
Thread.Sleep(1500);
Console.WriteLine("这是后台线程调用");
}
}
}运行上面的代码,可以看到DoRun2方法的打印信息“这是后台线程调用”将不会被显示出来,因为应用程序执行完主线程和前台线程后,就自动退出了,所有的后台线程将被自动终止。这里后台线程设置了等待1.5s,假如这个后台线程比前台线程或主线程提前执行完毕,对应的信息“这是后台线程调用”将可以被成功打印出来。
Task
.NET 4.0推出了新一代的多线程模型Task。async/await特性是与Task紧密相关的,所以在了解async/await前必须充分了解Task的使用。这里将以一个简单的Demo来看一下Task的使用,同时与Thread的创建方式做一下对比。
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Web;
using System.Threading;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace TestApp
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine("主线程启动");
//.NET 4.5引入了Task.Run静态方法来启动一个线程
Task.Run(() => { Thread.Sleep(1000); Console.WriteLine("Task1启动"); });
//Task启动的是后台线程,假如要在主线程中等待后台线程执行完毕,可以调用Wait方法
Task task = Task.Run(() => { Thread.Sleep(500); Console.WriteLine("Task2启动"); });
task.Wait();
Console.WriteLine("主线程结束");
}
}
}首先,必须明确一点是Task启动的线程是后台线程,不过可以通过在Main方法中调用task.Wait()方法,使应用程序等待task执行完毕。Task与Thread的一个重要区分点是:Task底层是使用线程池的,而Thread每次实例化都会创建一个新的线程。这里可以通过这段代码做一次验证:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Web;
using System.Threading;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace TestApp
{
class Program
{
static void DoRun1()
{
Console.WriteLine("Thread Id =" + Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId);
}
static void DoRun2()
{
Thread.Sleep(50);
Console.WriteLine("Task调用Thread Id =" + Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId);
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
for (int i = 0; i < 50; i++)
{
new Thread(DoRun1).Start();
}
for (int i = 0; i < 50; i++)
{
Task.Run(() => { DoRun2(); });
}
//让应用程序不立即退出
Console.Read();
}
}
}运行代码,可以看到DoRun1()方法每次的Thread Id都是不同的,而DoRun2()方法的Thread Id是重复出现的。我们知道线程的创建和销毁是一个开销比较大的操作,Task.Run()每次执行将不会立即创建一个新线程,而是到CLR线程池查看是否有空闲的线程,有的话就取一个线程处理这个请求,处理完请求后再把线程放回线程池,这个线程也不会立即撤销,而是设置为空闲状态,可供线程池再次调度,从而减少开销。
Task<TResult>
Task<TResult>是Task的泛型版本,这两个之间的最大不同是Task<TResult>可以有一个返回值,看一下代码应该一目了然:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Web;
using System.Threading;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace TestApp
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine("主线程开始");
Task task = Task.Run(() => { Thread.Sleep(1000); return Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId.ToString(); });
Console.WriteLine(task.Result);
Console.WriteLine("主线程结束");
}
}
}Task<TResult>的实例对象有一个Result属性,当在Main方法中调用task.Result的时候,将等待task执行完毕并得到返回值,这里的效果跟调用task.Wait()是一样的,只是多了一个返回值。
async/await 特性
经过前面的铺垫,终于迎来了这篇文章的主角async/await,还是先通过代码来感受一下这两个特性的使用。
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Web;
using System.Threading;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace TestApp
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine("-------主线程启动-------");
Task task = GetLengthAsync();
Console.WriteLine("Main方法做其他事情");
Console.WriteLine("Task返回的值" + task.Result);
Console.WriteLine("-------主线程结束-------");
}
static async Task GetLengthAsync()
{
Console.WriteLine("GetLengthAsync Start");
string str = await GetStringAsync();
Console.WriteLine("GetLengthAsync End");
return str.Length;
}
static Task GetStringAsync()
{
return Task.Run(() => { Thread.Sleep(2000); return "finished"; });
}
}
}首先来看一下async关键字。async用来修饰方法,表明这个方法是异步的,声明的方法的返回类型必须为:void或Task或Task<TResult>。返回类型为Task的异步方法中无需使用return返回值,而返回类型为Task<TResult>的异步方法中必须使用return返回一个TResult的值,如上述Demo中的异步方法返回一个int。而返回类型可为void,则是为了和事件处理程序兼容,比如下面的示例:
public Form1()
{
InitializeComponent();
btnDo.Click += Down;
}
public async void Down(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
btnDo.Enabled = false;
string str = await Run();
labText.Text = str;
btnDo.Enabled = true;
}
public Task Run()
{
return Task.Run(() => { Thread.Sleep(5000); return DateTime.Now.ToString(); });
}再来看一下await关键字。await必须用来修饰Task或Task<TResult>,而且只能出现在已经用async关键字修饰的异步方法中。
通常情况下,async/await必须成对出现才有意义,假如一个方法声明为async,但却没有使用await关键字,则这个方法在执行的时候就被当作同步方法,这时编译器也会抛出警告提示async修饰的方法中没有使用await,将被作为同步方法使用。了解了关键字async\await的特点后,我们来看一下上述Demo在控制台会输入什么吧。

输出的结果已经很明确地告诉我们整个执行流程了。GetLengthAsync异步方法刚开始是同步执行的,所以"GetLengthAsync Start"字符串会被打印出来,直到遇到第一个await关键字,真正的异步任务GetStringAsync开始执行,await相当于起到一个标记/唤醒点的作用,同时将控制权放回给Main方法,"Main方法做其他事情"字符串会被打印出来。之后由于Main方法需要访问到task.Result,所以就会等待异步方法GetLengthAsync的执行,而GetLengthAsync又等待GetStringAsync的执行,一旦GetStringAsync执行完毕,就会回到await GetStringAsync这个点上执行往下执行,这时"GetLengthAsync End"字符串就会被打印出来。
当然,我们也可以使用下面的方法完成上面控制台的输出。
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Web;
using System.Threading;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace TestApp
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine("-------主线程启动-------");
Task task = GetLengthAsync();
Console.WriteLine("Main方法做其他事情");
Console.WriteLine("Task返回的值" + task.Result);
Console.WriteLine("-------主线程结束-------");
}
static Task GetLengthAsync()
{
Console.WriteLine("GetLengthAsync Start");
Task task = Task.Run(() => { string str = GetStringAsync().Result;
Console.WriteLine("GetLengthAsync End");
return str.Length; });
return task;
}
static Task GetStringAsync()
{
return Task.Run(() => { Thread.Sleep(2000); return "finished"; });
}
}
}对比两种方法,是不是async\await关键字的原理其实就是通过使用一个线程完成异步调用吗?答案是否定的。async关键字表明可以在方法内部使用await关键字,方法在执行到await前都是同步执行的,运行到await处就会挂起,并返回到Main方法中,直到await标记的Task执行完毕,才唤醒回到await点上,继续向下执行。更深入点的介绍可以查看文章末尾的参考文献。
async/await 实际应用
微软已经对一些基础类库的方法提供了异步实现,接下来将实现一个例子来介绍一下async/await的实际应用。
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Web;
using System.Threading;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Net;
namespace TestApp
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine("开始获取博客园首页字符数量");
Task task1 = CountCharsAsync("http://www.cnblogs.com");
Console.WriteLine("开始获取百度首页字符数量");
Task task2 = CountCharsAsync("http://www.baidu.com");
Console.WriteLine("Main方法中做其他事情");
Console.WriteLine("博客园:" + task1.Result);
Console.WriteLine("百度:" + task2.Result);
}
static async Task CountCharsAsync(string url)
{
WebClient wc = new WebClient();
string result = await wc.DownloadStringTaskAsync(new Uri(url));
return result.Length;
}
}
}参考文献:<IIIustrated C# 2012> 关于async/await的FAQ 《深入理解C#》
http://npoi.codeplex.com/documentation
免费,开源,无需安装 Office,功能强大,兼容性好,使用方便,可以在 Visual Studio 的 NuGet 管理器中直接搜索安装。
导出 Excel 简单示例:
HSSFWorkbook book = new HSSFWorkbook();
ISheet sheet = book.CreateSheet("工作表1");
IRow r0 = sheet.CreateRow(0);
r0.CreateCell(0).SetCellValue("行1列1");
r0.CreateCell(1).SetCellValue("行1列2");
IRow r1 = sheet.CreateRow(1);
r1.CreateCell(0).SetCellValue("行2列1");
r1.CreateCell(2).SetCellValue("行2列3");
MemoryStream ms = new MemoryStream();
book.Write(ms);
Response.AddHeader("Content-Disposition", string.Format("attachment; filename={0}.xls", "文件名"));
Response.BinaryWrite(ms.ToArray());
Response.End();
book = null;
ms.Close();
ms.Dispose();字体相关:
ICellStyle style = book.CreateCellStyle();
IFont font = book.CreateFont();
font.FontHeightInPoints = 20; // 字体大小
font.Color = HSSFColor.White.Index; // 字体颜色
style.SetFont(font);
style.FillForegroundColor = HSSFColor.Red.Index; // 背景色
style.FillPattern = FillPattern.SolidForeground;
cell.CellStyle = style;合并单元格:
CellRangeAddress cra = new CellRangeAddress(r - 1, r - 1, c - 1, c);
sheet.AddMergedRegion(cra);宽度自适应:
for (int i = 1; i < c; i++) {
sheet.AutoSizeColumn(i);
}函数:
cell.SetCellFormula("SUM(B2:B4)");顺便提一句,ICellStyle 和 IFont 最好一种样式一个变量先定义好再用,不要在循环里疯狂地 Create,否则超出数量(512个)会导致样式失效。
其它参考:http://www.ez2o.com/Blog/Post/csharp-Excel-NPOI-Font-Style
| 符号 | 规则 | 示例 |
= | 精确匹配 | location = /a 仅可以匹配 /a 这个 uri |
| 不带任何修饰符 | 前缀匹配 | location /a 可以匹配 /a、/ab、/a/b 等 uri |
~ 或 ~* | 正则匹配
|
|
如果有多个 location 块匹配同一个请求,Nginx 会优先选择精确匹配的块,其次是正则匹配,最后是前缀匹配。
~ 与 ~* 不分优先,视 location 位置先后来匹配。
1. 跨子域的iframe高度自适应
2. 完全跨域的iframe高度自适应
同域的我们可以轻松的做到
1. 父页面通过iframe的contentDocument或document属性访问到文档对象,进而可以取得页面的高度,通过此高度值赋值给iframe tag。
2. 子页面可以通过parent访问到父页面里引入的iframe tag,进而设置其高度。
但跨域的情况则不允许对子页面或父页面的文档进行访问(返回undefined),所以我们要做的就是打通或间接打通这个壁垒。
一、跨子域的iframe高度自适应
比如 'a.jd.com/3.html' 嵌入了 'b.jd.com/4.html',这种跨子域的页面
3.html
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 |
|
4.html
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 |
|
可以看到与上一篇对比,只要在两个页面里都加上document.domain就可以了
二、完全跨域的iframe高度自适应
分别有以下资源
- 页面 A:http://snandy.github.io/lib/iframe/A.html
- 页面 B:http://snandy.github.io/lib/iframe/B.html
- 页面 C:http://snandy.jd-app.com
- D.js:http://snandy.github.io/lib/iframe/D.js
这四个资源有如下关系
1. A里嵌入C,A和C是不同域的,即跨域iframe
2. C里嵌入B,C和B是不同域的,但A和B是同域的
3. C里嵌入D.js,D.js放在和A同域的项目里
通过一个间接方式实现,即通过一个隐藏的B.html来实现高度自适应。
A.html
嵌入页面C: http://snandy.jd-app.com
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 |
|
B.html
嵌入在C页面中,它是隐藏的,通过parent.parent访问到A,再改变A的iframe(C.html)高度,这是最关键的,因为A,B是同域的所以可以访问A的文档对象等。
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 |
|
C.html
嵌入在A中,和A不同域,要实现C的自适应,C多高则A里的iframe就设为多高。C里嵌入B.html 和 D.js
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 |
|
D.js
在页面C载入后计算其高度,然后将计算出的height赋值给C里引入的iframe(B.html)的src
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 |
|
线上示例:http://snandy.github.io/lib/iframe/A.html
我们继续讲解LINQ to SQL语句,这篇我们来讨论Group By/Having操作符和Exists/In/Any/All/Contains操作符。
Group By/Having操作符
适用场景:分组数据,为我们查找数据缩小范围。
说明:分配并返回对传入参数进行分组操作后的可枚举对象。分组;延迟
1.简单形式:
var q =
from p in db.Products
group p by p.CategoryID into g
select g;
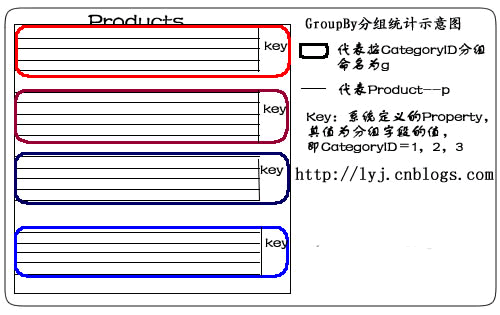
语句描述:使用Group By按CategoryID划分产品。
说明:from p in db.Products 表示从表中将产品对象取出来。group p by p.CategoryID into g表示对p按CategoryID字段归类。其结果命名为g,一旦重新命名,p的作用域就结束了,所以,最后select时,只能select g。当然,也不必重新命名可以这样写:
var q =
from p in db.Products
group p by p.CategoryID;
我们用示意图表示:
如果想遍历某类别中所有记录,这样:
foreach (var gp in q)
{
if (gp.Key == 2)
{
foreach (var item in gp)
{
//do something
}
}
}
2.Select匿名类:
var q =
from p in db.Products
group p by p.CategoryID into g
select new { CategoryID = g.Key, g };
说明:在这句LINQ语句中,有2个property:CategoryID和g。这个匿名类,其实质是对返回结果集重新进行了包装。把g的property封装成一个完整的分组。如下图所示:
如果想遍历某匿名类中所有记录,要这么做:
foreach (var gp in q)
{
if (gp.CategoryID == 2)
{
foreach (var item in gp.g)
{
//do something
}
}
}
3.最大值
var q =
from p in db.Products
group p by p.CategoryID into g
select new {
g.Key,
MaxPrice = g.Max(p => p.UnitPrice)
};
语句描述:使用Group By和Max查找每个CategoryID的最高单价。
说明:先按CategoryID归类,判断各个分类产品中单价最大的Products。取出CategoryID值,并把UnitPrice值赋给MaxPrice。
4.最小值
var q =
from p in db.Products
group p by p.CategoryID into g
select new {
g.Key,
MinPrice = g.Min(p => p.UnitPrice)
};
语句描述:使用Group By和Min查找每个CategoryID的最低单价。
说明:先按CategoryID归类,判断各个分类产品中单价最小的Products。取出CategoryID值,并把UnitPrice值赋给MinPrice。
5.平均值
var q =
from p in db.Products
group p by p.CategoryID into g
select new {
g.Key,
AveragePrice = g.Average(p => p.UnitPrice)
};
语句描述:使用Group By和Average得到每个CategoryID的平均单价。
说明:先按CategoryID归类,取出CategoryID值和各个分类产品中单价的平均值。
6.求和
var q =
from p in db.Products
group p by p.CategoryID into g
select new {
g.Key,
TotalPrice = g.Sum(p => p.UnitPrice)
};
语句描述:使用Group By和Sum得到每个CategoryID 的单价总计。
说明:先按CategoryID归类,取出CategoryID值和各个分类产品中单价的总和。
7.计数
var q =
from p in db.Products
group p by p.CategoryID into g
select new {
g.Key,
NumProducts = g.Count()
};
语句描述:使用Group By和Count得到每个CategoryID中产品的数量。
说明:先按CategoryID归类,取出CategoryID值和各个分类产品的数量。
8.带条件计数
var q =
from p in db.Products
group p by p.CategoryID into g
select new {
g.Key,
NumProducts = g.Count(p => p.Discontinued)
};
语句描述:使用Group By和Count得到每个CategoryID中断货产品的数量。
说明:先按CategoryID归类,取出CategoryID值和各个分类产品的断货数量。 Count函数里,使用了Lambda表达式,Lambda表达式中的p,代表这个组里的一个元素或对象,即某一个产品。
9.Where限制
var q =
from p in db.Products
group p by p.CategoryID into g
where g.Count() >= 10
select new {
g.Key,
ProductCount = g.Count()
};
语句描述:根据产品的―ID分组,查询产品数量大于10的ID和产品数量。这个示例在Group By子句后使用Where子句查找所有至少有10种产品的类别。
说明:在翻译成SQL语句时,在最外层嵌套了Where条件。
10.多列(Multiple Columns)
var categories =
from p in db.Products
group p by new
{
p.CategoryID,
p.SupplierID
}
into g
select new
{
g.Key,
g
};
语句描述:使用Group By按CategoryID和SupplierID将产品分组。
说明: 既按产品的分类,又按供应商分类。在by后面,new出来一个匿名类。这里,Key其实质是一个类的对象,Key包含两个Property:CategoryID、SupplierID。用g.Key.CategoryID可以遍历CategoryID的值。
11.表达式(Expression)
var categories =
from p in db.Products
group p by new { Criterion = p.UnitPrice > 10 } into g
select g;
语句描述:使用Group By返回两个产品序列。第一个序列包含单价大于10的产品。第二个序列包含单价小于或等于10的产品。
说明:按产品单价是否大于10分类。其结果分为两类,大于的是一类,小于及等于为另一类。
Exists/In/Any/All/Contains操作符
适用场景:用于判断集合中元素,进一步缩小范围。
Any
说明:用于判断集合中是否有元素满足某一条件;不延迟。(若条件为空,则集合只要不为空就返回True,否则为False)。有2种形式,分别为简单形式和带条件形式。
1.简单形式:
仅返回没有订单的客户:
var q =
from c in db.Customers
where !c.Orders.Any()
select c;
生成SQL语句为:
SELECT [t0].[CustomerID], [t0].[CompanyName], [t0].[ContactName],
[t0].[ContactTitle], [t0].[Address], [t0].[City], [t0].[Region],
[t0].[PostalCode], [t0].[Country], [t0].[Phone], [t0].[Fax]
FROM [dbo].[Customers] AS [t0]
WHERE NOT (EXISTS(
SELECT NULL AS [EMPTY] FROM [dbo].[Orders] AS [t1]
WHERE [t1].[CustomerID] = [t0].[CustomerID]
))
2.带条件形式:
仅返回至少有一种产品断货的类别:
var q =
from c in db.Categories
where c.Products.Any(p => p.Discontinued)
select c;
生成SQL语句为:
SELECT [t0].[CategoryID], [t0].[CategoryName], [t0].[Description],
[t0].[Picture] FROM [dbo].[Categories] AS [t0]
WHERE EXISTS(
SELECT NULL AS [EMPTY] FROM [dbo].[Products] AS [t1]
WHERE ([t1].[Discontinued] = 1) AND
([t1].[CategoryID] = [t0].[CategoryID])
)
All
说明:用于判断集合中所有元素是否都满足某一条件;不延迟
1.带条件形式
var q =
from c in db.Customers
where c.Orders.All(o => o.ShipCity == c.City)
select c;
语句描述:这个例子返回所有订单都运往其所在城市的客户或未下订单的客户。
Contains
说明:用于判断集合中是否包含有某一元素;不延迟。它是对两个序列进行连接操作的。
string[] customerID_Set =
new string[] { "AROUT", "BOLID", "FISSA" };
var q = (
from o in db.Orders
where customerID_Set.Contains(o.CustomerID)
select o).ToList();
语句描述:查找"AROUT", "BOLID" 和 "FISSA" 这三个客户的订单。 先定义了一个数组,在LINQ to SQL中使用Contains,数组中包含了所有的CustomerID,即返回结果中,所有的CustomerID都在这个集合内。也就是in。 你也可以把数组的定义放在LINQ to SQL语句里。比如:
var q = (
from o in db.Orders
where (
new string[] { "AROUT", "BOLID", "FISSA" })
.Contains(o.CustomerID)
select o).ToList();
Not Contains则取反:
var q = (
from o in db.Orders
where !(
new string[] { "AROUT", "BOLID", "FISSA" })
.Contains(o.CustomerID)
select o).ToList();
1.包含一个对象:
var order = (from o in db.Orders
where o.OrderID == 10248
select o).First();
var q = db.Customers.Where(p => p.Orders.Contains(order)).ToList();
foreach (var cust in q)
{
foreach (var ord in cust.Orders)
{
//do something
}
}
语句描述:这个例子使用Contain查找哪个客户包含OrderID为10248的订单。
2.包含多个值:
string[] cities =
new string[] { "Seattle", "London", "Vancouver", "Paris" };
var q = db.Customers.Where(p=>cities.Contains(p.City)).ToList();
语句描述:这个例子使用Contains查找其所在城市为西雅图、伦敦、巴黎或温哥华的客户。
总结一下这篇我们说明了以下语句:
| Group By/Having | 分组数据;延迟 |
| Any | 用于判断集合中是否有元素满足某一条件;不延迟 |
| All | 用于判断集合中所有元素是否都满足某一条件;不延迟 |
| Contains | 用于判断集合中是否包含有某一元素;不延迟 |
本系列链接:LINQ体验系列文章导航
LINQ推荐资源
LINQ专题:http://kb.cnblogs.com/zt/linq/ 关于LINQ方方面面的入门、进阶、深入的文章。
LINQ小组:http://space.cnblogs.com/group/linq/ 学习中遇到什么问题或者疑问提问的好地方。
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-transitional.dtd">
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml">
<head>
<title>标签示例</title>
<style type="text/css">
BODY { font-size: 14px; font-family: "宋体"; }
OL LI { margin: 8px; }
#con { font-size: 12px; margin: 0px auto; width: 600px; }
#tags { padding-right: 0px; padding-left: 0px; padding-bottom: 0px; margin: 0px 0px 0px 10px; width: 400px; padding-top: 0px; height: 23px; }
#tags LI { background: url(images/tagleft.gif) no-repeat left bottom; float: left; margin-right: 1px; list-style-type: none; height: 23px; }
#tags LI A { padding-right: 10px; padding-left: 10px; background: url(images/tagright.gif) no-repeat right bottom; float: left; padding-bottom: 0px; color: #999; line-height: 23px; padding-top: 0px; height: 23px; text-decoration: none; }
#tags LI.emptyTag { background: none transparent scroll repeat 0% 0%; width: 4px; }
#tags LI.selectTag { background-position: left top; margin-bottom: -2px; position: relative; height: 25px; }
#tags LI.selectTag A { background-position: right top; color: #000; line-height: 25px; height: 25px; }
#tagContent { border-right: #aecbd4 1px solid; padding-right: 1px; border-top: #aecbd4 1px solid; padding-left: 1px; padding-bottom: 1px; border-left: #aecbd4 1px solid; padding-top: 1px; border-bottom: #aecbd4 1px solid; background-color: #fff; }
.tagContent { padding-right: 10px; display: none; padding-left: 10px; background: url(images/bg.gif) repeat-x; padding-bottom: 10px; width: 576px; color: #474747; padding-top: 10px; height: 350px; }
#tagContent DIV.selectTag { display: block; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="con">
<ul id="tags">
<li><a onclick="selectTag('tagContent0',this)" href="javascript:void(0)">标签一</a>
</li>
<li class="selectTag"><a onclick="selectTag('tagContent1',this)" href="javascript:void(0)">
标签二</a> </li>
<li><a onclick="selectTag('tagContent2',this)" href="javascript:void(0)">自适应宽度的标签</a>
</li>
</ul>
<div id="tagContent">
<div class="tagContent" id="tagContent0">
第一个标签的内容</div>
<div class="tagContent selectTag" id="tagContent1">
第二个标签的内容</div>
<div class="tagContent" id="tagContent2">
第三个标签的内容</div>
</div>
</div>
<script type="text/javascript">
function selectTag(showContent, selfObj) {
// 操作标签
var tag = document.getElementById("tags").getElementsByTagName("li");
var taglength = tag.length;
for (i = 0; i < taglength; i++) {
tag[i].className = "";
}
selfObj.parentNode.className = "selectTag";
// 操作内容
for (i = 0; j = document.getElementById("tagContent" + i); i++) {
j.style.display = "none";
}
document.getElementById(showContent).style.display = "block";
}
</script>
</body>
</html>