制作类似下图中的拖拽排序功能:

1. 首先数据库该表中添加字段 sort,类型为 double(MySQL 中为 double(0, 0))。
2. 页面输出绑定数据(以 ASP.NET MVC 控制器为例):
public ActionResult EditSort()
{
if (!zConsole.Logined) { return RedirectToAction("", "SignIn", new { redirect = Request.Url.OriginalString }); }
db_auto2018Entities db = new db_auto2018Entities();
return View(db.dt_dealer.Where(c => c.enabled).OrderBy(c => c.sort));
}这里可以加条件列出,即示例中 enabled == true 的数据。
3. 前台页面引用 jQuery 和 jQuery UI。
4. 使用 <ul /> 列出数据:
<ul id="sortable" class="list-group gutter list-group-lg list-group-sp">
@foreach (var d in Model)
{
<li class="list-group-item" draggable="true" data-id="@d.id">
<span class="pull-left"><i class="fa fa-sort text-muted fa m-r-sm"></i> </span>
<div class="clear">
【id=@d.id】@d.name_full
</div>
</li>
}
</ul>5. 初始化 sortable,当拖拽结束时保存次序:
<script>
var url_SaveSort = '@Url.Action("SaveSort")';
</script>
<script>
$("#sortable").sortable({
stop: function (event, ui) {
// console.log('index: ' + $(ui.item).index())
// console.log('id: ' + $(ui.item).data('id'))
// console.log('prev_id: ' + $(ui.item).prev().data('id'))
$.post(url_SaveSort, {
id: $(ui.item).data('id'),
prev_id: $(ui.item).prev().data('id')
}, function (json) {
if (json.result.success) {
// window.location.reload();
} else {
toastr["error"](json.result.info);
}
}, 'json');
}
});
$("#sortable").disableSelection();
</script>这里回传到服务端的参数为:当前项的 id 值、拖拽后其前面一项的 prev_id 值(若移至首项则 prev_id 为 undefined)。
不使用 $(ui.item).index() 是因为,在有筛选条件的结果集中排序时,使用该索引值配合 LINQ 的 .Skip 会引起取值错误。
6. 控制器接收并保存至数据库:
[HttpPost]
public ActionResult SaveSort(int id, int? prev_id)
{
if (!zConsole.Logined)
{
return Json(new { result = new { success = false, msg = "请登录后重试!" } }, JsonRequestBehavior.AllowGet);
}
db_auto2018Entities db = new db_auto2018Entities();
dt_dealer d = db.dt_dealer.Find(id);
// 拖拽后其前项 sort 值(若无则 null)(此处不需要加 enabled 等筛选条件)
double? prev_sort = prev_id.HasValue
? db.dt_dealer.Where(c => c.id == prev_id).Select(c => c.sort).Single()
: null as double?;
// 拖拽后其后项 sort 值(若无前项则取首项作为后项)(必须强制转化为 double?,否则无后项时会返回 0,导致逻辑错误)
double? next_sort = prev_id.HasValue
? db.dt_dealer.Where(c => c.sort > prev_sort && c.id != id).OrderBy(c => c.sort).Select(c => (double?)c.sort).FirstOrDefault()
: db.dt_dealer.Where(c => c.id != id).OrderBy(c => c.sort).Select(c => (double?)c.sort).FirstOrDefault();
if (prev_sort.HasValue && next_sort.HasValue)
{
d.sort = (prev_sort.Value + next_sort.Value) / 2;
}
if (prev_sort == null && next_sort.HasValue)
{
d.sort = next_sort.Value - 1;
}
if (prev_sort.HasValue && next_sort == null)
{
d.sort = prev_sort.Value + 1;
}
db.SaveChanges();
return Json(new { item = new { id = d.id }, result = new { success = true } });
}需要注意的是,当往数据库添加新项时,必须将 sort 值设置为已存在的最大 sort 值 +1 或最小 sort 值 -1。
var d = new dt_dealer
{
name_full = "新建项",
sort = (db.dt_dealer.Max(c => (double?)c.sort) ?? 0) + 1,
};如果在 Visual Studio 2017 中打开 LINQ To SQL 的 .dbml 文件时是以 XML 的方式打开的,那么需要安装“LINQ to SQL tools”,步骤如下:
1,关闭 VS
2,运行 VS 安装程序
3,修改

4,切换到“单个组件”选项卡,勾选“LING to SQL 工具”

5,确认修改
推荐:参考此文:如何升级 ASP.NET 项目 MySql.Data 和 Connector/NET 至 8.0.x
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
这是 MySQL 官方提供的,用来帮助 .NET 开发者使用 LINQ 来方便操作 MySQL 数据库的解决方案。
我们所需要的软件全部被封装在 MySQL Installer 套件当中,非常方便。
下载后选择“Custom”自定义选择需要安装的产品和功能:
MySQL Server - 在本机安装 MySQL 数据库,如果我们直接连接远程数据库则不需要安装
MySQL for Visual Studio - 是一款 Visual Studio 插件,用于连接和管理 MySQL 数据库
Connector/NET - ADO.NET 托管提供程序
使用也非常方便:
在“服务资源管理器”中添加连接,更改数据源为“MySQL”。(如果没有该项,重启计算机试试;仍然没有,重新运行 MySQL Installer,选择“Modify ...”,勾选对应 VS 版本的“Visual Studio Integration”和“Entity Framework Designer Integration”)
项目中“添加新项”,在“数据”中选择“ADO.NET 实体数据模型”,即 Entity Framework,而非“LINQ to SQL 类”,根据需要选择表、视图和存储过程
Windows Server 服务器上安装 MySQL Server 过程中(或安装完成后再次运行 MySQL Installer)可配置端口(同时配置防火墙)。
建议勾选安装 MySQL Workbench 来管理 MySQL 数据库。
新建用户时,主机填“%”即该用户允许远程连接。
如果报以下错误:
不支持直接到存储查询(DbSet、DbQuery、DbSqlQuery)的数据绑定。应使用数据填充 DbSet (例如通过对 DbSet 调用 Load),然后绑定到本地数据。对于 WPF,绑定到 DbSet.Local。对于 WinForms,绑定到 DbSet.Local.ToBindingList()。
记得在绑定时加一个 .ToList() 即可。
如果发布后报以下错误:
找不到请求的 .Net Framework Data Provider。可能没有安装。
那么在服务器上安装 Connector/NET 即可。
如果在 VS 中连接此 EF 时如果遇到:
您的项目引用了最新版的实体框架;但是,找不到进行数据连接所需的与此版本兼容的实体框架数据库提供程序。请退出向导,安装兼容提供程序,重新生成您的项目,然后再执行此操作。
或
指定的架构无效。错误 0152: 未找到具有固定名称“MySql.Data.MySqlClient”的 ADO.NET 提供程序的实体框架提供程序。请确保在应用程序配置文件的“entityFramework”节中注册了该提供程序。有关详细信息,请参阅 http://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkId=260882。
那么,只需在 NuGet 中搜索并重新安装 MySql.Data.Entity ,重新生成项目。如果仍然提示,请检查 Connector/NET 是否有更新。
6.10.4 版本相关的问题参:MySQL Connector/Net 6.10.4 不支持 VS
先上代码
DataClassesXDataContext db = new DataClassesXDataContext();
// 使用 let 关键字
DateTime dt = DateTime.Now;
var q1 = (from z in db.dtZone
let adCount = db.dtAD.Count(ad => ad.iZone == z.ID)
select new
{
z.ID,
adCount,
}).Take(10).ToList();
Response.Write((DateTime.Now - dt) + "<br />");
// 先 Select 后 Take
dt = DateTime.Now;
var q2 = (from z in db.dtZone
select new
{
z.ID,
adCount = db.dtAD.Count(ad => ad.iZone == z.ID),
}).Take(10).ToList();
Response.Write((DateTime.Now - dt) + "<br />");
// 先 Take 后 Select
dt = DateTime.Now;
var q3 = (from z in db.dtZone
select new { z.ID }).Take(10).ToList().Select(z => new
{
z.ID,
adCount = db.dtAD.Count(ad => ad.iZone == z.ID),
}).ToList();
Response.Write((DateTime.Now - dt) + "<br />");在一个有 365 行记录的 dtZone 表和 5700 行记录的 dtAD 的数据库中进行嵌套查询(远程),同样取 10 条 dtZone 记录及对应的 dtAD 数,结果表明前两种执行时间相差无几,第二种略快,但第三种由于进行了多次查询,消耗的时间接近于前两种的 10 倍。结果仅供参考。
有时候已知一个 ID 的数组,需要读取这些记录内容,SQL 可以联接多个“或”关系去读取,或使用“In”语句,在 LINQ TO SQL 中可以这样来做:
List<int> ids = new List<int> { 1, 2, 3 };
List<string> tbs = db.dbTables.Where(c => ids.Contains<int>(c.ID)).ToList();
我们继续讲解LINQ to SQL语句,这篇我们来讨论Group By/Having操作符和Exists/In/Any/All/Contains操作符。
Group By/Having操作符
适用场景:分组数据,为我们查找数据缩小范围。
说明:分配并返回对传入参数进行分组操作后的可枚举对象。分组;延迟
1.简单形式:
var q =
from p in db.Products
group p by p.CategoryID into g
select g;
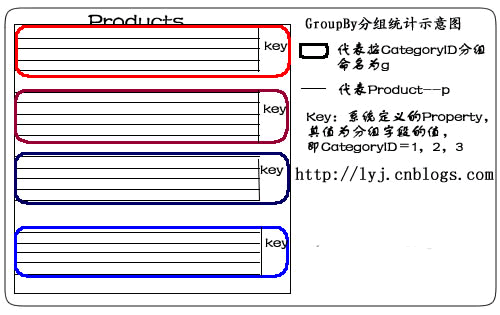
语句描述:使用Group By按CategoryID划分产品。
说明:from p in db.Products 表示从表中将产品对象取出来。group p by p.CategoryID into g表示对p按CategoryID字段归类。其结果命名为g,一旦重新命名,p的作用域就结束了,所以,最后select时,只能select g。当然,也不必重新命名可以这样写:
var q =
from p in db.Products
group p by p.CategoryID;
我们用示意图表示:
如果想遍历某类别中所有记录,这样:
foreach (var gp in q)
{
if (gp.Key == 2)
{
foreach (var item in gp)
{
//do something
}
}
}
2.Select匿名类:
var q =
from p in db.Products
group p by p.CategoryID into g
select new { CategoryID = g.Key, g };
说明:在这句LINQ语句中,有2个property:CategoryID和g。这个匿名类,其实质是对返回结果集重新进行了包装。把g的property封装成一个完整的分组。如下图所示:
如果想遍历某匿名类中所有记录,要这么做:
foreach (var gp in q)
{
if (gp.CategoryID == 2)
{
foreach (var item in gp.g)
{
//do something
}
}
}
3.最大值
var q =
from p in db.Products
group p by p.CategoryID into g
select new {
g.Key,
MaxPrice = g.Max(p => p.UnitPrice)
};
语句描述:使用Group By和Max查找每个CategoryID的最高单价。
说明:先按CategoryID归类,判断各个分类产品中单价最大的Products。取出CategoryID值,并把UnitPrice值赋给MaxPrice。
4.最小值
var q =
from p in db.Products
group p by p.CategoryID into g
select new {
g.Key,
MinPrice = g.Min(p => p.UnitPrice)
};
语句描述:使用Group By和Min查找每个CategoryID的最低单价。
说明:先按CategoryID归类,判断各个分类产品中单价最小的Products。取出CategoryID值,并把UnitPrice值赋给MinPrice。
5.平均值
var q =
from p in db.Products
group p by p.CategoryID into g
select new {
g.Key,
AveragePrice = g.Average(p => p.UnitPrice)
};
语句描述:使用Group By和Average得到每个CategoryID的平均单价。
说明:先按CategoryID归类,取出CategoryID值和各个分类产品中单价的平均值。
6.求和
var q =
from p in db.Products
group p by p.CategoryID into g
select new {
g.Key,
TotalPrice = g.Sum(p => p.UnitPrice)
};
语句描述:使用Group By和Sum得到每个CategoryID 的单价总计。
说明:先按CategoryID归类,取出CategoryID值和各个分类产品中单价的总和。
7.计数
var q =
from p in db.Products
group p by p.CategoryID into g
select new {
g.Key,
NumProducts = g.Count()
};
语句描述:使用Group By和Count得到每个CategoryID中产品的数量。
说明:先按CategoryID归类,取出CategoryID值和各个分类产品的数量。
8.带条件计数
var q =
from p in db.Products
group p by p.CategoryID into g
select new {
g.Key,
NumProducts = g.Count(p => p.Discontinued)
};
语句描述:使用Group By和Count得到每个CategoryID中断货产品的数量。
说明:先按CategoryID归类,取出CategoryID值和各个分类产品的断货数量。 Count函数里,使用了Lambda表达式,Lambda表达式中的p,代表这个组里的一个元素或对象,即某一个产品。
9.Where限制
var q =
from p in db.Products
group p by p.CategoryID into g
where g.Count() >= 10
select new {
g.Key,
ProductCount = g.Count()
};
语句描述:根据产品的―ID分组,查询产品数量大于10的ID和产品数量。这个示例在Group By子句后使用Where子句查找所有至少有10种产品的类别。
说明:在翻译成SQL语句时,在最外层嵌套了Where条件。
10.多列(Multiple Columns)
var categories =
from p in db.Products
group p by new
{
p.CategoryID,
p.SupplierID
}
into g
select new
{
g.Key,
g
};
语句描述:使用Group By按CategoryID和SupplierID将产品分组。
说明: 既按产品的分类,又按供应商分类。在by后面,new出来一个匿名类。这里,Key其实质是一个类的对象,Key包含两个Property:CategoryID、SupplierID。用g.Key.CategoryID可以遍历CategoryID的值。
11.表达式(Expression)
var categories =
from p in db.Products
group p by new { Criterion = p.UnitPrice > 10 } into g
select g;
语句描述:使用Group By返回两个产品序列。第一个序列包含单价大于10的产品。第二个序列包含单价小于或等于10的产品。
说明:按产品单价是否大于10分类。其结果分为两类,大于的是一类,小于及等于为另一类。
Exists/In/Any/All/Contains操作符
适用场景:用于判断集合中元素,进一步缩小范围。
Any
说明:用于判断集合中是否有元素满足某一条件;不延迟。(若条件为空,则集合只要不为空就返回True,否则为False)。有2种形式,分别为简单形式和带条件形式。
1.简单形式:
仅返回没有订单的客户:
var q =
from c in db.Customers
where !c.Orders.Any()
select c;
生成SQL语句为:
SELECT [t0].[CustomerID], [t0].[CompanyName], [t0].[ContactName],
[t0].[ContactTitle], [t0].[Address], [t0].[City], [t0].[Region],
[t0].[PostalCode], [t0].[Country], [t0].[Phone], [t0].[Fax]
FROM [dbo].[Customers] AS [t0]
WHERE NOT (EXISTS(
SELECT NULL AS [EMPTY] FROM [dbo].[Orders] AS [t1]
WHERE [t1].[CustomerID] = [t0].[CustomerID]
))
2.带条件形式:
仅返回至少有一种产品断货的类别:
var q =
from c in db.Categories
where c.Products.Any(p => p.Discontinued)
select c;
生成SQL语句为:
SELECT [t0].[CategoryID], [t0].[CategoryName], [t0].[Description],
[t0].[Picture] FROM [dbo].[Categories] AS [t0]
WHERE EXISTS(
SELECT NULL AS [EMPTY] FROM [dbo].[Products] AS [t1]
WHERE ([t1].[Discontinued] = 1) AND
([t1].[CategoryID] = [t0].[CategoryID])
)
All
说明:用于判断集合中所有元素是否都满足某一条件;不延迟
1.带条件形式
var q =
from c in db.Customers
where c.Orders.All(o => o.ShipCity == c.City)
select c;
语句描述:这个例子返回所有订单都运往其所在城市的客户或未下订单的客户。
Contains
说明:用于判断集合中是否包含有某一元素;不延迟。它是对两个序列进行连接操作的。
string[] customerID_Set =
new string[] { "AROUT", "BOLID", "FISSA" };
var q = (
from o in db.Orders
where customerID_Set.Contains(o.CustomerID)
select o).ToList();
语句描述:查找"AROUT", "BOLID" 和 "FISSA" 这三个客户的订单。 先定义了一个数组,在LINQ to SQL中使用Contains,数组中包含了所有的CustomerID,即返回结果中,所有的CustomerID都在这个集合内。也就是in。 你也可以把数组的定义放在LINQ to SQL语句里。比如:
var q = (
from o in db.Orders
where (
new string[] { "AROUT", "BOLID", "FISSA" })
.Contains(o.CustomerID)
select o).ToList();
Not Contains则取反:
var q = (
from o in db.Orders
where !(
new string[] { "AROUT", "BOLID", "FISSA" })
.Contains(o.CustomerID)
select o).ToList();
1.包含一个对象:
var order = (from o in db.Orders
where o.OrderID == 10248
select o).First();
var q = db.Customers.Where(p => p.Orders.Contains(order)).ToList();
foreach (var cust in q)
{
foreach (var ord in cust.Orders)
{
//do something
}
}
语句描述:这个例子使用Contain查找哪个客户包含OrderID为10248的订单。
2.包含多个值:
string[] cities =
new string[] { "Seattle", "London", "Vancouver", "Paris" };
var q = db.Customers.Where(p=>cities.Contains(p.City)).ToList();
语句描述:这个例子使用Contains查找其所在城市为西雅图、伦敦、巴黎或温哥华的客户。
总结一下这篇我们说明了以下语句:
| Group By/Having | 分组数据;延迟 |
| Any | 用于判断集合中是否有元素满足某一条件;不延迟 |
| All | 用于判断集合中所有元素是否都满足某一条件;不延迟 |
| Contains | 用于判断集合中是否包含有某一元素;不延迟 |
本系列链接:LINQ体验系列文章导航
LINQ推荐资源
LINQ专题:http://kb.cnblogs.com/zt/linq/ 关于LINQ方方面面的入门、进阶、深入的文章。
LINQ小组:http://space.cnblogs.com/group/linq/ 学习中遇到什么问题或者疑问提问的好地方。
Earlier this summer I started writing a multi-part blog series that discusses the built-in LINQ to SQL provider in .NET 3.5. LINQ to SQL is an ORM (object relational mapping) implementation that allows you to model a relational database using .NET classes. You can then query the database using LINQ, as well as update/insert/delete data from it. LINQ to SQL fully supports transactions, views, and stored procedures. It also provides an easy way to integrate data validation and business logic rules into your data model.
You can learn more about LINQ to SQL by reading my posts below (more will be coming soon):
- Part 1: Introduction to LINQ to SQL
- Part 2: Defining our Data Model Classes
- Part 3: Querying our Database
- Part 4: Updating our Database
- Part 5: Binding UI using the ASP:LinqDataSource Control
Using the LINQ to SQL Debug Visualizer
One of the nice development features that LINQ to SQL supports is the ability to use a "debug visualizer" to hover over a LINQ expression while in the VS 2008 debugger and inspect the raw SQL that the ORM will ultimately execute at runtime when evaluating the LINQ query expression.
For example, assume we write the below LINQ query expression code against a set of data model classes:
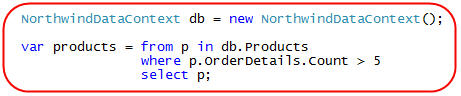
We could then use the VS 2008 debugger to hover over the "products" variable after the query expression has been assigned:
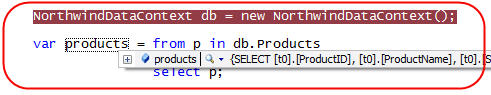
And if we click the small magnifying glass in the expression above, we can launch the LINQ to SQL debug visualizer to inspect the raw SQL that the ORM will execute based on that LINQ query:
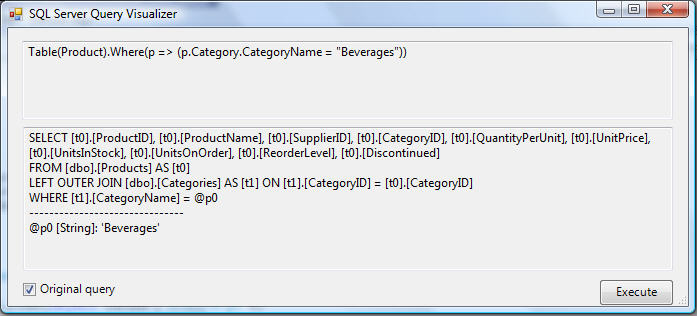
If you click the "Execute" button, you can even test out the SQL query and see the raw returned results that will be returned from the database:
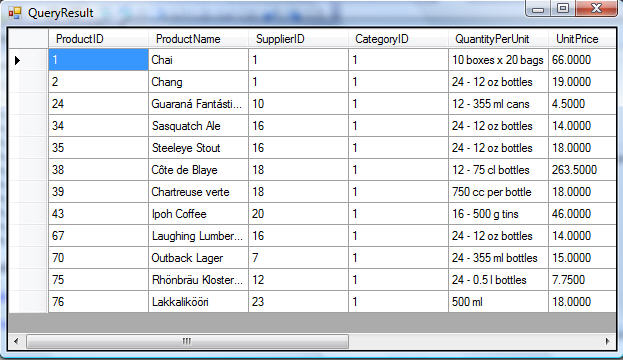
This obviously makes it super easy to see precisely what SQL query logic LINQ to SQL ORM is doing for you.
You can learn even more about how all this works by reading the Part 3: Querying our Database segment in my LINQ to SQL series above.
How to Install the LINQ to SQL Debug Visualizer
The LINQ to SQL Debug Visualizer isn't built-in to VS 2008 - instead it is an add-in that you need to download to use. You can download a copy of it here.
The download contains both a binary .dll assembly version of the visualizer (within the \bin\debug directory below), as well as all of the source code for the visualizer:
To install the LINQ to SQL debug visualizer, follow the below steps:
1) Shutdown all running versions of Visual Studio 2008
2) Copy the SqlServerQueryVisualizer.dll assembly from the \bin\debug\ directory in the .zip download above into your local \Program Files\Microsoft Visual Studio 9.0\Common7\Packages\Debugger\Visualizers\ directory:
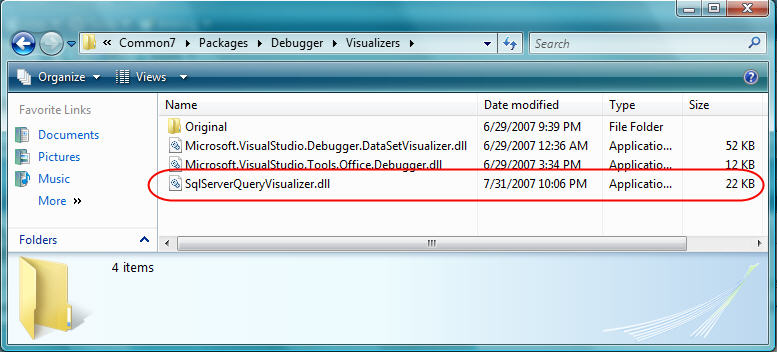
3) Start up Visual Studio 2008 again. Now when you use the debugger with LINQ to SQL you should be able to hover over LINQ query expressions and inspect their raw SQL (no extra registration is required).
Hope this helps,
Scott